Salvage Abdominoperineal Resection for Squamous Cell Anal Cancer: A 30-Year Single-Institution Experience
- PMID: 29691737
- PMCID: PMC5976705
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-018-6483-9
Salvage Abdominoperineal Resection for Squamous Cell Anal Cancer: A 30-Year Single-Institution Experience
Abstract
Background: Failure of chemoradiotherapy (CRT) for anal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) results in persistent or recurrent anal SCC. Treatment with salvage abdominoperineal resection (APR) can potentially achieve cure. The aims of this study are to analyze oncological and surgical outcomes of our 30-year experience with salvage APR for anal SCC after failed CRT and identify prognostic factors for overall survival (OS).
Methods: All consecutive patients who underwent salvage APR between 1990 and 2016 for histologically confirmed persistent or recurrent anal SCC after failed CRT were retrospectively analyzed.
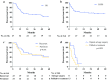
Results: Forty-seven patients underwent salvage APR for either persistent (n = 24) or recurrent SCC (n = 23). Median OS was 47 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 10.0-84.0 months] and 5-year survival was 41.6%, which did not differ significantly between persistent or recurrent disease (p = 0.551). Increased pathological tumor size (p < 0.001) and lymph node involvement (p = 0.014) were associated with impaired hazard for OS on multivariable analysis, and irradical resection only (p = 0.001) on univariable analysis. Twenty-one patients developed local recurrence after salvage APR, of whom 8 underwent repeat salvage surgery and 13 received palliative treatment. Median OS was 9 months (95% CI 7.2-10.8 months) after repeat salvage surgery and 4 months (95% CI 2.8-5.1 months) following palliative treatment (p = 0.055).
Conclusions: Salvage APR for anal SCC after failed CRT resulted in adequate survival, with 5-year survival of 41.6%. Negative prognostic factors for survival were increased tumor size, lymph node involvement, and irradical resection. Patients with recurrent anal SCC after salvage APR had poor prognosis, irrespective of performance of repeat salvage surgery, which never resulted in cure.
Figures

Comment in
-
ASO Author Reflections: Salvage Surgery for Anal Cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2018 Dec;25(Suppl 3):852-853. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-7025-1. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30414037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Survival following salvage abdominoperineal resection for persistent and recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the anus: do these disease categories affect survival?Colorectal Dis. 2016 Oct;18(10):959-966. doi: 10.1111/codi.13288. Colorectal Dis. 2016. PMID: 26850085
-
A systematic review of outcomes after salvage abdominoperineal resection for persistent or recurrent anal squamous cell cancer.Colorectal Dis. 2019 Jun;21(6):632-650. doi: 10.1111/codi.14569. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Colorectal Dis. 2019. PMID: 30689272
-
Abdominoperineal resection for squamous cell anal carcinoma: survival and risk factors for recurrence.Ann Surg Oncol. 2012 Dec;19(13):4186-92. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2485-1. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22825769 Clinical Trial.
-
Inguinal Lymph Node Dissection Does Not Improve Overall Survival in Anal Cancer Nodal Disease.J Surg Res. 2020 Nov;255:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.05.034. Epub 2020 Jun 12. J Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32540576
-
Management of Recurrent Anal Cancer.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2025 Jan;34(1):91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2024.07.005. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2025. PMID: 39547772 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesorectal failure after chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the anus: is sphincter-saving surgery reasonable?Tech Coloproctol. 2023 May;27(5):379-388. doi: 10.1007/s10151-022-02698-7. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Tech Coloproctol. 2023. PMID: 36127625
-
Executive Summary of the American Radium Society Appropriate Use Criteria for Treatment of Anal Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Nov 1;105(3):591-605. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.2544. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 31288054 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management of Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Anal Canal and Anal Margin After Failure of Chemoradiotherapy Treatment: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;17(9):1511. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091511. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of haematological parameters in predicting the response to radical chemoradiotherapy in patients with anal squamous cell cancer.Radiol Oncol. 2021 Oct 8;55(4):449-458. doi: 10.2478/raon-2021-0039. Radiol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34626531 Free PMC article.
-
Salvage Treatment of Recurrent or Persistent Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The Role of Multi-modality Therapy.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2024 Mar;23(1):85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2023.12.002. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38216367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Epidermoid Anal Cancer: results from the UKCCCR randomised trial of radiotherapy alone versus radiotherapy, 5-fluorouracil, and mitomycin. UKCCCR Anal Cancer Trial Working Party. UK Co-ordinating Committee on Cancer Research. Lancet. 1996;348(9034):1049–54. - PubMed
-
- Bartelink H, Roelofsen F, Eschwege F, et al. Concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy is superior to radiotherapy alone in the treatment of locally advanced anal cancer: results of a phase III randomized trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Radiotherapy and Gastrointestinal Cooperative Groups. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(5):2040–2049. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.5.2040. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Flam M, John M, Pajak TF, et al. Role of mitomycin in combination with fluorouracil and radiotherapy, and of salvage chemoradiation in the definitive nonsurgical treatment of epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal: results of a phase III randomized intergroup study. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14(9):2527–2539. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.9.2527. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

