Congenital Titinopathy: Comprehensive characterization and pathogenic insights
- PMID: 29691892
- PMCID: PMC6105519
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25241
Congenital Titinopathy: Comprehensive characterization and pathogenic insights
Abstract
Objective: Comprehensive clinical characterization of congenital titinopathy to facilitate diagnosis and management of this important emerging disorder.
Methods: Using massively parallel sequencing we identified 30 patients from 27 families with 2 pathogenic nonsense, frameshift and/or splice site TTN mutations in trans. We then undertook a detailed analysis of the clinical, histopathological and imaging features of these patients.
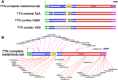
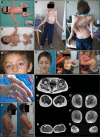
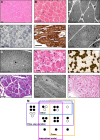
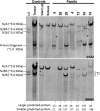
Results: All patients had prenatal or early onset hypotonia and/or congenital contractures. None had ophthalmoplegia. Scoliosis and respiratory insufficiency typically developed early and progressed rapidly, whereas limb weakness was often slowly progressive, and usually did not prevent independent walking. Cardiac involvement was present in 46% of patients. Relatives of 2 patients had dilated cardiomyopathy. Creatine kinase levels were normal to moderately elevated. Increased fiber size variation, internalized nuclei and cores were common histopathological abnormalities. Cap-like regions, whorled or ring fibers, and mitochondrial accumulations were also observed. Muscle magnetic resonance imaging showed gluteal, hamstring and calf muscle involvement. Western blot analysis showed a near-normal sized titin protein in all samples. The presence of 2 mutations predicted to impact both N2BA and N2B cardiac isoforms appeared to be associated with greatest risk of cardiac involvement. One-third of patients had 1 mutation predicted to impact exons present in fetal skeletal muscle, but not included within the mature skeletal muscle isoform transcript. This strongly suggests developmental isoforms are involved in the pathogenesis of this congenital/early onset disorder.
Interpretation: This detailed clinical reference dataset will greatly facilitate diagnostic confirmation and management of patients, and has provided important insights into disease pathogenesis. Ann Neurol 2018;83:1105-1124.
© 2018 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to report.
Figures
References
-
- Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, et al. The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700‐kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z‐line to I‐band linking system. Circ Res 2001;89:1065–1072. - PubMed
-
- Labeit S, Kolmerer B. Titins: giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science 1995;270:293–296. - PubMed
-
- Whiting A, Wardale J, Trinick J. Does titin regulate the length of muscle thick filaments? J Mol Biol 1989;205:263–268. - PubMed
-
- Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J. Titin: properties and family relationships. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003;4:679–689. - PubMed
-
- Ehler E, Gautel M. The sarcomere and sarcomerogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol 2008;642:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

