Non-canonical functions of the RB protein in cancer
- PMID: 29692417
- PMCID: PMC6693677
- DOI: 10.1038/s41568-018-0008-5
Non-canonical functions of the RB protein in cancer
Abstract
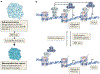
The canonical model of RB-mediated tumour suppression developed over the past 30 years is based on the regulation of E2F transcription factors to restrict cell cycle progression. Several additional functions have been proposed for RB, on the basis of which a non-canonical RB pathway can be described. Mechanistically, the non-canonical RB pathway promotes histone modification and regulates chromosome structure in a manner distinct from cell cycle regulation. These functions have implications for chemotherapy response and resistance to targeted anticancer agents. This Opinion offers a framework to guide future studies of RB in basic and clinical research.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

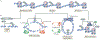

References
-
- Dyson N The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 12, 2245–2262 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Classon M & Harlow E The retinoblastoma tumour suppressor in development and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 910–917 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ Cancer cell cycles. Science 274, 1672–1677 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ & McCormick F The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell 2, 103–112 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

