Conventional Versus Giant Basal Cell Carcinoma, a Review of 57 Cases: Histologic Differences Contributing to Excessive Growth
- PMID: 29692457
- PMCID: PMC5903045
- DOI: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_165_17
Conventional Versus Giant Basal Cell Carcinoma, a Review of 57 Cases: Histologic Differences Contributing to Excessive Growth
Abstract
Background: Giant basal cell carcinoma (GBCC) is defined as a basal cell carcinoma (BCC) exceeding 5 cm in size. While these tumors impart significant morbidity due to local tissue destruction and have a higher rate of metastatic disease than their conventional (smaller) counterparts, reasons for their large size remain unclear. While theories relating to neglect or faster growth rate are often invoked; to date, there has not been a comprehensive evaluation of the histologic features of these large tumors that may contribute to their size.
Methods: Histologic features of GBCCs (n = 29) were evaluated and compared to those of conventional BCC (n = 28). Available clinical demographic data were also reviewed.
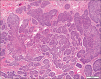
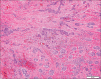
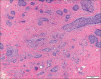
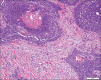
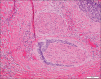
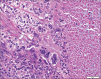
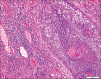
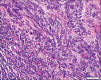
Results: GBCCs, in addition to overall larger size, more often were thicker, displayed ulceration, and showed a more infiltrative growth pattern than their conventional counterparts. These rare tumors also displayed an insignificant increased propensity for a brisk host immune response, and the infiltrate significantly more often included clusters of plasma cells.
Conclusions: Most histologic features seen in GBCCs likely reflect their large size. Histologic features alone are unlikely to explain the size of these rare tumors. The possibility of an altered host immune response contributing to the growth of these tumors requires further investigation.
Keywords: Basal cell carcinoma; giant basal cell carcinoma; host immune response; plasma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest. What is new? The histologic features of giant basal cell carcinoma reflect their large size, with increased overall size, tumor depth, and ulceration compared to conventional BCC.Tumor microenvironment may provide clues to giant BCC capacity for large size.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Giant Basal Cell Carcinomas Arising on the Bilateral Forearms of a Patient: A Case Report and Review of Nonsurgical Treatment Options.Case Rep Dermatol. 2016 Dec 13;8(3):363-368. doi: 10.1159/000452323. eCollection 2016 Sep-Dec. Case Rep Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 28101025 Free PMC article.
-
Giant Basal Cell Carcinomas Express Neuroactive Mediators and Show a High Growth Rate: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis of Etiopathogenic and Prognostic Factors.Am J Dermatopathol. 2017 Mar;39(3):189-194. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000640. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017. PMID: 27759693 Free PMC article.
-
When basal cell carcinomas became giant: an Italian multicenter study.Int J Dermatol. 2020 Mar;59(3):377-382. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14728. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Int J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31774173
-
Reappraisal of giant basal cell carcinoma: Clinical features and outcomes.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020 Jan;73(1):53-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2019.06.029. Epub 2019 Jun 28. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020. PMID: 31519500
-
Giant basal cell carcinoma of the skin: literature review and personal experience.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012 Aug;26(8):942-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04427.x. Epub 2011 Dec 28. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012. PMID: 22211959 Review.
Cited by
-
Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Patient and Physician's Experience.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018 Sep;8(3):329-337. doi: 10.1007/s13555-018-0245-2. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018. PMID: 29860652 Free PMC article.
-
Complex reconstruction of the orbitofrontal regions using three regional flaps after orbital exenteration for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan-Mar;64(1):57-61. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32292859 Free PMC article.
-
Giant Mushroom-like Neglected Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Shoulder with Spontaneous Bleeding: A Successful Surgical Approach.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2021 Dec 22;8(12):003089. doi: 10.12890/2021_003089. eCollection 2021. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 35059348 Free PMC article.
-
Resection of Skin Cancer Resulting in Free Vascularized Tissue Reconstruction: Always a Therapeutic Failure?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 25;15(9):2464. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092464. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173928 Free PMC article.
-
Giant basal cell carcinoma located in the temporal region: delay of the patient's visit because of COVID-19 pandemic.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2024 Nov 18;42(2):203-205. doi: 10.5114/ada.2024.144485. eCollection 2025 Apr. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2024. PMID: 40521059 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Archontaki M, Stavrianos SD, Korkolis DP, Arnogiannaki N, Vassiliadis V, Liapakis IE, et al. Giant basal cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of 51 cases and review of the literature. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2655–63. - PubMed
-
- Nasser N, Nasser Filho N, Trauczynski Neto B, Silva LM. Giant basal cell carcinoma. An Bras Dermatol. 2012;87:469–71. - PubMed
-
- Randle HW, Roenigk RK, Brodland DG. Giant basal cell carcinoma (T3). Who is at risk? Cancer. 1993;72:1624–30. - PubMed
-
- Anwar U, Al Ghazal SK, Ahmad M, Sharpe DT. Horrifying basal cell carcinoma forearm lesion leading to shoulder disarticulation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117:6e–9e. - PubMed
-
- Randle HW. Basal cell carcinoma. Identification and treatment of the high-risk patient. Dermatol Surg. 1996;22:255–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
