Spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, pneumorrhachis, pneumoretroperitoneum, surgical emphysema
- PMID: 29692541
- PMCID: PMC5894309
- DOI: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_168_17
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, pneumorrhachis, pneumoretroperitoneum, surgical emphysema
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
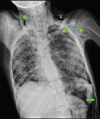
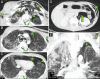
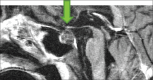
References
-
- Jougon JB, Ballester M, Delcambre F, Mac Bride T, Dromer CE, Velly JF. Assessment of spontaneous pneumomediastinum: Experience with 12 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:1711–4. - PubMed
-
- Takada K, Matsumoto S, Hiramatsu T, Kojima E, Watanabe H, Sizu M, et al. Management of spontaneous pneumomediastinum based on clinical experience of 25 cases. Respir Med. 2008;102:1329–34. - PubMed
-
- Burn JM, Guyer PB, Langdon L. The spread of solutions injected into the epidural space; a study using epidurograms in patients with lumbosciatic syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 1973;45:338–45. - PubMed
-
- Alves A, Panis Y, Pocard M. Management of anastomotic leakage after nondiverted large bowel resection. J Am Coll Surg. 1999;189:554–9. - PubMed
-
- Aghayev E, Yen K, Sonnenschein M, Jackowski C, Thali M, Vock P, et al. Pneumomediastinum and soft tissue emphysema of the neck in postmortem CT and MRI; a new vital sign in hanging? Forensic Sci Int. 2005;153:181–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

