Tributyltin and Zebrafish: Swimming in Dangerous Water
- PMID: 29692757
- PMCID: PMC5903028
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00152
Tributyltin and Zebrafish: Swimming in Dangerous Water
Abstract
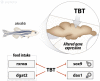
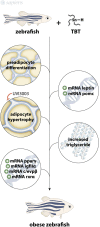
Zebrafish has been established as a reliable biological model with important insertion in academy (morphologic, biochemical, and pathophysiological studies) and pharmaceutical industry (toxicology and drug development) due to its molecular complexity and similar systems biology that recapitulate those from other organisms. Considering the toxicological aspects, many efforts using zebrafish models are being done in order to elucidate the effects of endocrine disruptors, and some of them are focused on tributyltin (TBT) and its mechanism of action. TBT is an antifouling agent applied in ship's hull that is constantly released into the water and absorbed by marine organisms, leading to bioaccumulation and biomagnification effects. Thus, several findings of malformations and changes in the normal biochemical and physiologic aspects of these marine animals have been related to TBT contamination. In the present review, we have compiled the most significant studies related to TBT effects in zebrafish, also taking into consideration the effects found in other study models.
Keywords: endocrine disruptors; imposex; obesogenic; tributyltin; zebrafish.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elucidating the mechanism of action of tributyltin (TBT) in zebrafish.Aquat Toxicol. 2011 May;103(1-2):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Aquat Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21388611
-
Effects of Tributyltin and Other Retinoid Receptor Agonists in Reproductive-Related Endpoints in the Zebrafish (Danio rerio).J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2015;78(12):747-60. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2015.1028301. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2015. PMID: 26090559
-
Environmental management aspects for TBT antifouling wastes from the shipyards.J Environ Manage. 2009 Feb;90 Suppl 1:S77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.07.017. Epub 2008 Oct 31. J Environ Manage. 2009. PMID: 18951695
-
Environmental levels, toxicity and human exposure to tributyltin (TBT)-contaminated marine environment. a review. b_antizar@hotmail.com.Environ Int. 2008 Feb;34(2):292-308. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.09.005. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Environ Int. 2008. PMID: 17959247 Review.
-
Predicting the fate and effects of tributyltin in marine systems.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000;166:1-48. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 10868075 Review.
Cited by
-
Zebrafish Larvae as a Behavioral Model in Neuropharmacology.Biomedicines. 2019 Mar 26;7(1):23. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines7010023. Biomedicines. 2019. PMID: 30917585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Health and Toxicology: Immunomodulation Promoted by Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Tributyltin.Toxics. 2023 Aug 12;11(8):696. doi: 10.3390/toxics11080696. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37624201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tavares B, Santos Lopes S. The importance of zebrafish in biomedical research. Acta Med Port (2013) 26(5):583–92. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

