Case-based review: pediatric medulloblastoma
- PMID: 29692919
- PMCID: PMC5909805
- DOI: 10.1093/nop/npx011
Case-based review: pediatric medulloblastoma
Abstract
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor affecting children. These tumors are high grade with propensity to metastasize within the central nervous system and, less frequently, outside the neuraxis. Recent advancements in molecular subgrouping of medulloblastoma refine diagnosis and improve counseling in regards to overall prognosis. Both are predicated on the molecular drivers of each subgroup-WNT-activated, SHH-activated, group 3, and group 4. The traditional therapeutic mainstay for medulloblastoma includes a multimodal approach with surgery, radiation, and multiagent chemotherapy. As we discover more about the molecular basis of medulloblastoma, efforts to adjust treatment approaches based on molecular risk stratification are under active investigation. Certainly, the known neurological, developmental, endocrine, and psychosocial injury related to medulloblastoma and its associated therapies motivate ongoing research towards improving treatment for this life-threatening tumor while at the same time minimizing long-term side effects.
Keywords: chemotherapy; medulloblastoma; radiation; risk stratification; targeted therapy.
Figures

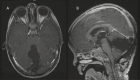
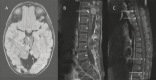


References
-
- Curran EK, Sainani KL, Le GM, et al. Gender affects survival for medulloblastoma only in older children and adults: a study from the surveillance epidemiology and end results registry. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;52(1):60–64. - PubMed
-
- Smith MJ, Beetz C, Williams SG, et al. Germline mutations in SUFU cause Gorlin syndrome-associated childhood medulloblastoma and redefine the risk associated with PTCH1 mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(36):4155–4161. - PubMed
-
- Taylor MD, Mainprize TG, Rutka JT. Molecular insight into medulloblastoma and central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor biology from hereditary syndromes: a review. Neurosurgery. 2000;47(4):888–901. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

