Modelling Cooperative Tumorigenesis in Drosophila
- PMID: 29693007
- PMCID: PMC5859872
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4258387
Modelling Cooperative Tumorigenesis in Drosophila
Abstract
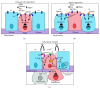
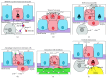
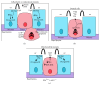
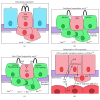
The development of human metastatic cancer is a multistep process, involving the acquisition of several genetic mutations, tumour heterogeneity, and interactions with the surrounding microenvironment. Due to the complexity of cancer development in mammals, simpler model organisms, such as the vinegar fly, Drosophila melanogaster, are being utilized to provide novel insights into the molecular mechanisms involved. In this review, we highlight recent advances in modelling tumorigenesis using the Drosophila model, focusing on the cooperation of oncogenes or tumour suppressors, and the interaction of mutant cells with the surrounding tissue in epithelial tumour initiation and progression.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

