Attitudes of undergraduate medical students toward mental illnesses and psychiatry
- PMID: 29693031
- PMCID: PMC5903151
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_87_17
Attitudes of undergraduate medical students toward mental illnesses and psychiatry
Abstract
Background: Worldwide, studies show negative attitude among medical students toward psychiatry and mental illness. The knowledge of the attitude and awareness of the undergraduate medical students toward psychiatry, mental health, and psychiatric disorders are most important as they are going to be involved in the care of these patients either directly or indirectly during the later years of their careers.
Aim: This study aims to assess attitude toward psychiatry and mental illness among undergraduate medical students.
Methodology: The responses of 67 medical students from the 6th semester (third professional year) batch who completed their 2-week clinical posting of psychiatry in 4th semester (i.e., second professional year) were collected using validated questionnaires, attitude towards mental illness (AMI), and attitude towards psychiatry (ATP) that assessed their attitudes to psychiatry and mental illness. Double data entry and validation were done using EpiData and analysis using Epi Info software.
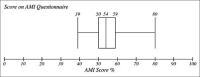
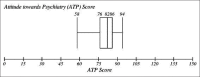
Results: Median AMI score was 54 (out of maximum 100) showing a neutral AMI. Median ATP score was 82 (out of maximum 150) also showing a neutral ATP. The theme-wise analysis showed that the attitude of students toward psychiatrist and psychiatry branch was relatively better compared to their AMI.
Conclusion: Undergraduate students have a neutral attitude to psychiatry and mental illness. More efforts are needed to change the attitude to favorable side.
Keywords: Attitude; medical students; mental illness; psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The World Health Report 2001. Mental Health: New Understanding; New Hope. Geneva: WHO; 2001.
-
- Gururaj G, Varghese M, Benegal V, Rao GN, Pathak K, Singh LK, et al. National Mental Health Survey of India, 2015-16: Summary. National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences. NIMHANS Publication No. 128. 2016
-
- Rezler AG. Methods of attitude assessment for medical teachers. Med Educ. 1976;10:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Khan SA, Yousafzai AU, Mehir RK, Inam-ul-Haq Attitude of medical students towards psychiatry in NWFP. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2008;20:44–6. - PubMed
-
- Malhi GS, Parker GB, Parker K, Carr VJ, Kirkby KC, Yellowlees P, et al. Attitudes toward psychiatry among students entering medical school. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2003;107:424–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources