A translational model of chronic kidney disease in swine
- PMID: 29693449
- PMCID: PMC6442373
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00063.2018
A translational model of chronic kidney disease in swine
Abstract
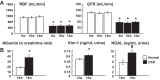
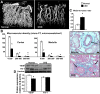
Animal models of chronic kidney disease (CKD) are critical for understanding its pathophysiology and for therapeutic development. The cardiovascular and renal anatomy and physiology of the pig are virtually identical to humans. This study aimed to develop a novel translational model of CKD that mimics the pathological features of CKD in humans. CKD was induced in seven domestic pigs by bilateral renal artery stenosis and diet-induced dyslipidemia. Animals were observed for a total of 14 wk. Renal hemodynamics and function were quantified in vivo using multi-detector CT after 6, 10, and 14 wk of CKD. Urine and blood were collected at each time-point, and blood pressure was continuously measured (telemetry). After completion of in vivo studies, pigs were euthanized, kidneys were removed, and microvascular (MV) architecture (μCT), markers of renal injury, inflammation, and fibrosis were evaluated ex vivo. Additional pigs were used as controls ( n = 7). Renal blood flow and glomerular filtration were reduced by 50% in CKD, accompanied by hypertension and elevated plasma creatinine, albumin-to-creatinine ratio and increased urinary KIM-1 and NGAL, suggesting renal injury. Furthermore, 14 wk of CKD resulted in cortical and medullary MV remodeling and loss, inflammation, glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy, and tubule-interstitial fibrosis compared with controls. The current study characterizes a novel model of CKD that mimics several of the pathological features observed in human CKD, irrespective of the etiology. Current approaches only slow rather than halt CKD progression, and this novel model may offer a suitable platform for the development of new treatments in a translational fashion.
Keywords: chronic renal disease; fibrosis; inflammation; microcirculation; renal hemodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures



References
-
- Bábíčková J, Klinkhammer BM, Buhl EM, Djudjaj S, Hoss M, Heymann F, Tacke F, Floege J, Becker JU, Boor P. Regardless of etiology, progressive renal disease causes ultrastructural and functional alterations of peritubular capillaries. Kidney Int 91: 70–85, 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.07.038. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

