Nanotechnological Strategies for Protein Delivery
- PMID: 29693640
- PMCID: PMC6100203
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23051008
Nanotechnological Strategies for Protein Delivery
Abstract
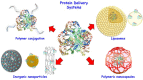
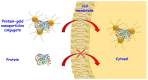
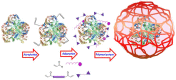
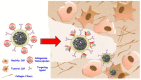
The use of therapeutic proteins plays a fundamental role in the treatment of numerous diseases. The low physico-chemical stability of proteins in physiological conditions put their function at risk in the human body until they reach their target. Moreover, several proteins are unable to cross the cell membrane. All these facts strongly hinder their therapeutic effect. Nanomedicine has emerged as a powerful tool which can provide solutions to solve these limitations and improve the efficacy of treatments based on protein administration. This review discusses the advantages and limitations of different types of strategies employed for protein delivery, such as PEGylation, transport within liposomes or inorganic nanoparticles or their in situ encapsulation.
Keywords: PEGylation; liposomes; nanoparticles; polymeric nanocapsules; protein delivery system; protein therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

