Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide in Subjects With Hepatic Impairment
- PMID: 29693715
- PMCID: PMC6175428
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.1131
Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide in Subjects With Hepatic Impairment
Abstract
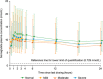
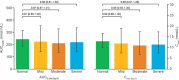
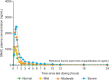
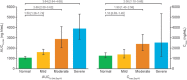
Semaglutide is a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog that has been co-formulated with the absorption enhancer, sodium N-(8-[2-hydroxybenzoyl] amino) caprylate, for oral administration. This trial (NCT02016911) investigated whether hepatic impairment affects the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide. Subjects were classified into groups: normal hepatic function (n = 24), and mild (n = 12), moderate (n = 12), or severe (n = 8) hepatic impairment according to Child-Pugh criteria, and received once-daily oral semaglutide (5 mg for 5 days followed by 10 mg for 5 days). Semaglutide plasma concentrations were measured during dosing and for up to 21 days post-last dose. Area under the semaglutide plasma concentration-time curve from 0-24 hours after the 10th dose (primary end point) and maximum semaglutide concentration after the 10th dose appeared similar across hepatic function groups. Similarly, there was no apparent effect of hepatic impairment on time to maximum semaglutide concentration (median range 1.0-1.5 hours) or half-life (geometric mean range 142-156 hours). No safety concerns were identified in subjects with hepatic impairment receiving semaglutide. Reported adverse events were in line with those observed for other glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. There was no apparent effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of oral semaglutide. The results of this trial suggest that dose adjustment of oral semaglutide is not warranted in subjects with hepatic impairment.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonists; hepatic impairment; pharmacokinetics; semaglutide.
© 2018, The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures

References
-
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. The incretin system: glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2006;368:1696–1705. - PubMed
-
- Verspohl EJ. Novel therapeutics for type 2 diabetes: incretin hormone mimetics (glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists) and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;124:113–138. - PubMed
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient‐centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

