Lack of Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease to Cynomolgus Macaques
- PMID: 29695429
- PMCID: PMC6026755
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00550-18
Lack of Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease to Cynomolgus Macaques
Abstract
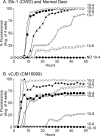
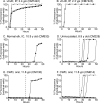
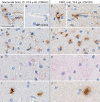
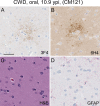
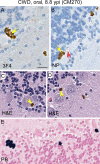
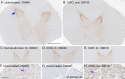
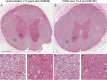
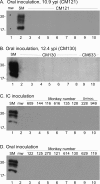
Chronic wasting disease (CWD) is a fatal prion disease that can infect deer, elk, and moose. CWD was first recognized in captive deer kept in wildlife facilities in Colorado from 1967 to 1979. CWD has now been detected in 25 U.S. states, 2 Canadian provinces, South Korea, Norway, and Finland. It is currently unknown if humans are susceptible to CWD infection. Understanding the health risk from consuming meat and/or products from CWD-infected cervids is a critical human health concern. Previous research using transgenic mouse models and in vitro conversion assays suggests that a significant species barrier exists between CWD and humans. To date, reported epidemiologic studies of humans consuming cervids in areas where CWD is endemic have found no evidence to confirm CWD transmission to humans. Previously, we reported data from ongoing cross-species CWD transmission studies using two species of nonhuman primates as models. Squirrel monkeys (SM) and cynomolgus macaques (CM) were inoculated by either the intracerebral or oral route with brain homogenates from CWD-infected deer and elk containing high levels of infectivity. SM were highly susceptible to CWD infection, while CM were not. In the present study, we present new data for seven CWD-inoculated CM euthanized 11 to 13 years after CWD inoculation and eight additional uninoculated control CM. New and archival CM tissues were screened for prion infection by using the ultrasensitive real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) assay, immunohistochemistry, and immunoblotting. In this study, there was no clinical, pathological, or biochemical evidence suggesting that CWD was transmitted from cervids to CM.IMPORTANCE Chronic wasting disease (CWD) is a fatal prion disease found in deer, elk, and moose. Since it was first discovered in the late 1960s, CWD has now spread to at least 25 U.S. states, 2 Canadian provinces, South Korea, Norway, and Finland. Eradication of CWD from areas of endemicity is very unlikely, and additional spread will occur. As the range and prevalence of CWD increase, so will the potential for human exposure to CWD prions. It is currently unknown if CWD poses a risk to human health. However, determining this risk is critical to preventing a scenario similar to that which occurred when mad cow disease was found to be transmissible to humans. In the present study, we used cynomolgus macaque monkeys as a surrogate model for CWD transmission to humans. After 13 years, no evidence for CWD transmission to macaques was detected clinically or by using highly sensitive prion disease-screening assays.
Keywords: CWD strains; RT-QuIC; barrier; chronic wasting disease; cross-species transmission; cynomolgus macaques; prion; squirrel monkeys.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

