Dual-responsive dithio-polydopamine coated porous CeO2 nanorods for targeted and synergistic drug delivery
- PMID: 29695903
- PMCID: PMC5905827
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S152002
Dual-responsive dithio-polydopamine coated porous CeO2 nanorods for targeted and synergistic drug delivery
Abstract
Objective: The aim was to produce the first report of assembling degradable stimuli-responsive dithio-polydopamine coating with a cancer target unit for synergistic and targeted drug delivery.
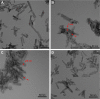
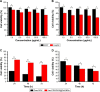
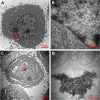
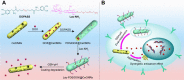
Methods: A multifunctional drug delivery system was constructed by coating a dual-responsive dithio-polydopamine (PDS) on porous CeO2 nanorods and subsequent conjugation of lactose derivative, where the PDS was formed by self-polymerization of dithio-dopamine (DOPASS).
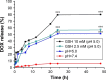
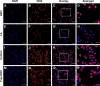
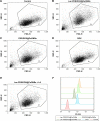
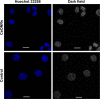
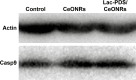
Results: The multifunctional drug delivery system displayed excellent cancer targeted ability resulting from the conjugation of lactose derivative, which could specifically recognize the overexpressed asialoglycoprotein receptors on the surface of HepG2 cells. It also showed a dual-responsive property of glutathione and pH, achieving controllable drug release from the cleavage of disulfide bond and subsequent degradation of PDS in cancer cells. Moreover, the degradation of PDS led to the exposure of CeO2 nanorods, which has a synergistic anticancer effect due to its cytotoxicity to cancer cells.
Conclusion: This work presents a good example of a rational design towards synergistic and targeted DDS for cancer chemotherapies.
Keywords: cerium oxide nanoparticles; degradable polydopamine; dual-responsiveness; synergistic anticancer; targeted drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Chang Y, Yang K, Wei P, et al. Cationic vesicles based on amphiphilic pillar[5]arene capped with ferrocenium: a redox-responsive system for drug/siRNA co-delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53(48):13126–13130. - PubMed
-
- Hu X-Y, Liu X, Zhang W, et al. Controllable construction of biocompatible supramolecular micelles and vesicles by water-soluble phosphate pillar[5,6]arenes for selective anti-cancer drug delivery. Chem Mater. 2016;28(11):3778–3788.
-
- Chi X, Ji X, Shao L, Huang F. A multiresponsive amphiphilic supramolecular diblock copolymer based on pillar[10]arene/paraquat complexation for rate-tunable controlled release. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2017;38(4):1600626. - PubMed
-
- Yu G, Yu W, Shao L, et al. Fabrication of a targeted drug delivery system from a pillar[5]arene-based supramolecular diblock copolymeric amphiphile for effective cancer therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(48):8999–9008.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

