Efficacy of pemetrexed-based regimens in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations after tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure: a systematic review
- PMID: 29695919
- PMCID: PMC5905532
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S157370
Efficacy of pemetrexed-based regimens in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations after tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure: a systematic review
Abstract
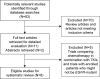
Pemetrexed-based chemotherapy regimens (pem regimens) are the standard first-line treatment option in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The objective of this systematic review was to assess the efficacy of pemetrexed in the context of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive NSCLC following the failure of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment. We searched biomedical literature databases (PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane library) and conference proceedings for studies evaluating the efficacy of pemetrexed monotherapy or pemetrexed combined with platinum or any other chemotherapeutic agent in EGFR-mutation-positive NSCLC after EGFR-TKI failure. We extracted data of primary outcomes of interest (progression-free survival [PFS], overall survival [OS], and overall response rate [ORR]). The weighted median PFS, OS, and ORR were then calculated. Of 83 potentially relevant studies, eight (three randomized studies and five retrospective studies) were identified (involving 1,193 patients) and included in this systematic review, with 640 patients receiving pem regimens. The weighted median PFS, median OS, and ORR for patients treated with pem regimens were 5.09 months, 15.91 months, and 30.19%, respectively. Our systematic review results showed a favorable efficacy profile of pem regimens in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation after EGFR-TKI failure.
Keywords: advanced non–small cell lung cancer; epidermal growth factor receptor; pemetrexed; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure LLY, XW, and LDY are employees of Eli Lilly and Company. HBH was involved in the design and conduct of the systematic literature review, funded by Eli Lilly and Company. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Park S, Keam B, Kim SH, et al. Pemetrexed singlet versus nonpemetrexed-based platinum doublet as second-line chemotherapy after first- line epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure in non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations. Cancer Res Treat. 2015;47(4):630–637. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Masuda T, Imai H, Kuwako T, et al. Efficacy of platinum combination chemotherapy after first-line gefitinib treatment in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring sensitive EGFR mutations. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015;17(9):702–709. - PubMed
-
- Lee SJ, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K, Ahn MJ. Pemetrexed plus platinum versus pemetrexed alone in non-small cell lung cancer patients who have progressed after first-line EGFR TKIs. Lung Cancer. 2015;90(2):261–266. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous