GLYX-13 Ameliorates Schizophrenia-Like Phenotype Induced by MK-801 in Mice: Role of Hippocampal NR2B and DISC1
- PMID: 29695955
- PMCID: PMC5904356
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00121
GLYX-13 Ameliorates Schizophrenia-Like Phenotype Induced by MK-801 in Mice: Role of Hippocampal NR2B and DISC1
Abstract
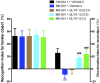
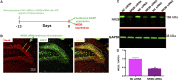
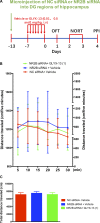
Background: Evidence supports that the hypofunction of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) and downregulation of disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) contribute to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. N-Methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B (NR2B)-containing NMDAR are associated with cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. GLYX-13 is an NMDAR glycine-site functional partial agonist and cognitive enhancer that does not induce psychotomimetic side effects. However, it remains unclear whether NR2B plays a critical role in the GLYX-13-induced alleviation of schizophrenia-like behaviors in mice. Methods: The effect of GLYX-13 was tested by observing changes in locomotor activity, novel object recognition ability, and prepulse inhibition (PPI) induced by dizocilpine (known as MK-801) in mice. Lentivirus-mediated NR2B knockdown in the hippocampus was assessed to confirm the role of NR2B in GLYX-13 pathophysiology, using Western blots and immunohistochemistry. Results: The systemic administration of GLYX-13 (0.5 and 1 mg/kg, i.p.) ameliorates MK-801 (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.)-induced hyperlocomotion, deficits in memory, and PPI in mice. Additionally, GLYX-13 normalized the MK-801-induced alterations in signaling molecules, including NR2B and DISC1 in the hippocampus. Furthermore, we found that NR2B knockdown produced memory and PPI deficits without any changes in locomotor activity. Notably, DISC1 levels significantly decreased by NR2B knockdown. However, the effective dose of GLYX-13 did not alleviate the memory and PPI dysfunctions or downregulation of DISC1 induced by NR2B knockdown. Conclusion: Our results suggest GLYX-13 as a candidate for schizophrenia treatment, and NR2B and DISC1 in the hippocampus may account for the molecular mechanisms of GLYX-13.
Keywords: GLYX-13; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1; schizophrenia.
Figures






Comment in
-
Commentary: GLYX-13 Ameliorates Schizophrenia-Like Phenotype Induced by MK-801 in Mice: Role of Hippocampal NR2B and DISC1.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Sep 5;11:315. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00315. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30233316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akashi K., Kakizaki T., Kamiya H., Fukaya M., Yamasaki M., Abe M., et al. (2009). NMDA receptor GluN2B (GluR epsilon 2/NR2B) subunit is crucial for channel function, postsynaptic macromolecular organization, and actin cytoskeleton at hippocampal CA3 synapses. J. Neurosci. 29 10869–10882. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5531-08.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brigman J. L., Wright T., Talani G., Prasad-Mulcare S., Jinde S., Seabold G. K., et al. (2010). Loss of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in CA1 hippocampus and cortex impairs long-term depression, reduces dendritic spine density, and disrupts learning. J. Neurosci. 30 4590–4600. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0640-10.2010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaperon F., Müller W., Auberson Y. P., Tricklebank M. D., Neijt H. C. (2003). Substitution for PCP, disruption of prepulse inhibition and hyperactivity induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists: preferential involvement of the NR2B rather than NR2A subunit. Behav. Pharmacol. 14 477–487. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

