Conserved Histidine Adjacent to the Proximal Cluster Tunes the Anaerobic Reductive Activation of Escherichia coli Membrane-Bound [NiFe] Hydrogenase-1
- PMID: 29696103
- PMCID: PMC5900901
- DOI: 10.1002/celc.201800047
Conserved Histidine Adjacent to the Proximal Cluster Tunes the Anaerobic Reductive Activation of Escherichia coli Membrane-Bound [NiFe] Hydrogenase-1
Abstract
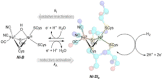
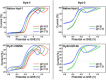
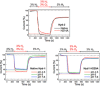
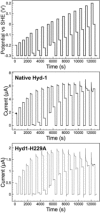
[NiFe] hydrogenases are electrocatalysts that oxidize H2 at a rapid rate without the need for precious metals. All membrane-bound [NiFe] hydrogenases (MBH) possess a histidine residue that points to the electron-transfer iron sulfur cluster closest ("proximal") to the [NiFe] H2-binding active site. Replacement of this amino acid with alanine induces O2 sensitivity, and this has been attributed to the role of the histidine in enabling the reversible O2-induced over-oxidation of the [Fe4S3Cys2] proximal cluster possessed by all O2-tolerant MBH. We have created an Escherichia coli Hyd-1 His-to-Ala variant and report O2-free electrochemical measurements at high potential that indicate the histidine-mediated [Fe4S3Cys2] cluster-opening/closing mechanism also underpins anaerobic reactivation. We validate these experiments by comparing them to the impact of an analogous His-to-Ala replacement in Escherichia coli Hyd-2, a [NiFe]-MBH that contains a [Fe4S4] center.
Keywords: bioinorganic chemistry; electrochemistry; electron transfer; hydrogen; metalloenzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrochemical insights into the mechanism of NiFe membrane-bound hydrogenases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Feb;44(1):315-28. doi: 10.1042/BST20150201. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 26862221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of the iron-sulfur cluster proximal to the active site on the catalytic function of an O2-tolerant NAD(+)-reducing [NiFe]-hydrogenase.Biochemistry. 2015 Jan 20;54(2):389-403. doi: 10.1021/bi501347u. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Biochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25517969
-
Reactivation from the Ni-B state in [NiFe] hydrogenase of Ralstonia eutropha is controlled by reduction of the superoxidised proximal cluster.Chem Commun (Camb). 2016 Feb 11;52(12):2632-5. doi: 10.1039/c5cc10382g. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016. PMID: 26750202
-
Proton Transfer Pathways between Active Sites and Proximal Clusters in the Membrane-Bound [NiFe] Hydrogenase.J Phys Chem B. 2019 Apr 25;123(16):3409-3420. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b00617. Epub 2019 Apr 11. J Phys Chem B. 2019. PMID: 30931567
-
The Model [NiFe]-Hydrogenases of Escherichia coli.Adv Microb Physiol. 2016;68:433-507. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Adv Microb Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27134027 Review.
Cited by
-
De novo design of symmetric ferredoxins that shuttle electrons in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 16;116(29):14557-14562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905643116. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31262814 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Unusual Properties of the Master Regulator FNR in the Extreme Acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 19;10:1642. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01642. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31379789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin A., in The Metal-Driven Biogeochemistry of Gaseous Compounds in the Environment (Eds.: P. M. H. Kroneck, M. E. S. Torres), Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, 2014, pp. 99–124.
-
- None
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
