Burden of disease studies in the WHO European Region-a mapping exercise
- PMID: 29697771
- PMCID: PMC6093319
- DOI: 10.1093/eurpub/cky060
Burden of disease studies in the WHO European Region-a mapping exercise
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) have produced numerous global burden of disease (GBD) estimates since the 1990s, using disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs). Here we attempt to identify studies that have either independent DALY estimates or build on the work of WHO and IHME, for the WHO European Region, categorize them by scope of disease analysis and geographic coverage, and briefly compare their methodology (age weighting, discounting and disability weights).
Methods: Google and Google Scholar were used with the search terms 'DALY', 'national burden of disease', Member State names and researcher's names, covering all years. Studies were categorized as: 'specific' (fewer than five disease categories or just risk factors for a single country), 'specific, multicountry' (fewer than five disease categories or just risk factors for more than one country), 'extensive' (covering five or more but not all disease categories for one country), 'full, sub country' (covering all relevant disease categories for part of one country) and 'full, country' (covering all relevant disease categories for one country).
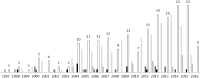
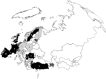
Results: A total of 198 studies were identified: 143 'specific', 26 'specific, multicountry', 7 'extensive', 10 'full, sub country' and 12 'full, country' [England (1), Estonia (2), France (1), Romania (1), Serbia (1), Spain (3), Sweden (2) and Turkey (1)]. About 5 (20%) of the 25 examinable 'extensive', 'full, sub country' and 'full, country' studies calculated DALYs using GBD 2010 methodology.
Conclusions: Independent burden of diseases studies in Europe have been located, and categorized by scope of disease analysis and geographic coverage. Methodological choices varied between independent 'full, country' studies.
Figures
References
-
- Last JM. A Dictionary of Public Health. New York: Oxford University Press, 2007.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, USA. Available at: http://www.healthdata.org/gbd/about/history (16 November 2017, date last accessed).
-
- Donev D, Zaletel-Kragelj L, Bjegovic V, Burazeri G. Measuring the burden of disease: disability adjusted life year (DALY) In: Zaletel-Kragelj L, Božikov J, editors. Methods and Tools in Public Health: A Handbook for Teachers, Researchers and Health Professionals. Lage: Hans Jacobs, 2010: 715–48.
-
- Mathers CD, Vos T, Lopez AD, et al. National Burden of Disease Studies: A Practical Guide, 2nd ednGeneva: World Health Organization, 2001.
-
- Prüss-Ustün A, Mathers C, Corvalán C, Woodward A. Introduction and Methods: Assessing the Environmental Burden of Disease at National and Local Levels, 1st ednGeneva: World Health Organization, 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

