Comparison of inflammatory markers between brucella and non-brucella epididymo-orchitis
- PMID: 29697933
- PMCID: PMC6092658
- DOI: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2018.0004.0
Comparison of inflammatory markers between brucella and non-brucella epididymo-orchitis
Abstract
Objectives: Brucellosis is a multi-system infectious disease that is associated with inflammation, which causes an increase in acute phase reactants. Hematological inflammatory markers of brucellosis include mean platelet volume (MPV), red cell distribution width (RDW), neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR). In this study, we aimed to evaluate the diagnostic value of hematological inflammatory markers in Brucella epididymo-orchitis (BEO), and to investigate the utility of these markers for differential diagnosis from non-Brucella epididymo-orchitis (non-BEO).
Materials and methods: We retrospectively reviewed the records of 22 BEO and 50 non-BEO patients. Hematological parameters were recorded and compared between the two groups. The main diagnostic criteria for BEO were positive clinical findings (i.e., testicular pain, tenderness and scrotal swelling), a positive Rose Bengal test result, standard tube agglutination (STA) titer ≥ 1/160, and/or a positive blood culture.
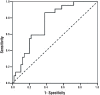
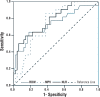
Results: The most decisive factors in discriminating between BEO and non-BEO were NLR, RDW, and MPV, in decreasing order of their strength. Regardless of other factors, NLR values < 2.3 significantly increased the odds of BEO (OR=8.080, 95% CI: 1.929- 33.843, p=0.004). After adjusting for other factors, RDW values >14.45% significantly increased the odds of BEO (OR=7.020, 95% CI: 1.749-28.176, p=0.006). Independent of the other factors, patients with MPV < 7.65 fL had a 6.336 times higher risk for BEO (95% CI: 1.393 - 28.822, p=0.017).
Conclusion: Hematological inflammatory markers such as NLR, RDW, and MPV can aid in the differential diagnosis of BEO and non-BEO.
Keywords: Brucella; Hematologic Neoplasms; Infectious Disease Medicine.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, Christou L, Tsianos EV. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:91–99. - PubMed
-
- Kanık-Yüksek S, Gülhan B, Ozkaya-Parlakay A, Tezer H. A case of childhood Brucellosis with neurological involvement and epididymo-orchitis. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2014;8:1636–1638. - PubMed
-
- Colmenero JD, Reguera JM, Martos F, Sánchez-De-Mora D, Delgado M, Causse M, et al. Complications associated with Brucella melitensis infection: a study of 530 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1996;75:195–211. Erratum in: Medicine (Baltimore) 1997;76:139. - PubMed
-
- Colmenero JD, Muñoz-Roca NL, Bermudez P, Plata A, Villalobos A, Reguera JM. Clinical findings, diagnostic approach, and outcome of Brucella melitensis epididymoorchitis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007;57:367–372. - PubMed
-
- Gul HC, Akyol I, Sen B, Adayener C, Haholu A. Epididymoorchitis due to Brucella melitensis: review of 19 patients. Urol Int. 2009;82:158–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources