Effects of N-Alkyl-4-Methylamphetamine Optical Isomers on Plasma Membrane Monoamine Transporters and Abuse-Related Behavior
- PMID: 29697951
- PMCID: PMC6051915
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00138
Effects of N-Alkyl-4-Methylamphetamine Optical Isomers on Plasma Membrane Monoamine Transporters and Abuse-Related Behavior
Abstract
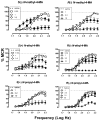
4-Methylamphetamine (4-MA) is an emerging drug of abuse that acts as a substrate at plasma membrane transporters for dopamine (DAT), norepinephrine (NET), and serotonin (SERT), thereby causing nonexocytotic release of monoamine transmitters via reverse transport. Prior studies by us showed that increasing the N-alkyl chain length of N-substituted 4-MA analogues converts 4-MA from a transportable substrate (i.e., releaser) at DAT and NET to a nontransported blocker at these sites. Here, we studied the effects of the individual optical isomers of N-methyl-, N-ethyl-, and N- n-propyl 4-MA on monoamine transporters and abuse-related behavior in rats because action/function might be related to stereochemistry. Uptake inhibition and release assays were conducted in rat brain synaptosomes whereas electrophysiological assessments of drug-transporter interactions were examined using cell-based biosensors. Intracranial-self-stimulation in rats was employed to assess abuse potential in vivo. The experimental evidence demonstrates that S(+) N-methyl 4-MA is a potent and efficacious releaser at DAT, NET, and SERT with the highest abuse potential among the test drugs, whereas R(-) N-methyl 4-MA is a less potent releaser with reduced abuse potential. The S(+)ethyl analogue has decreased efficacy as a releaser at DAT but retains full release activity at NET and SERT with a reduction in abuse-related effects; the R(-)ethyl analogue has a similar profile but is less potent. S(+) N-Propyl 4-MA is a nontransported blocker at DAT and NET but an efficacious releaser at SERT, whereas the R enantiomer is almost inactive. In conclusion, the S enantiomers of the N-alkyl 4-MA analogues are most potent. Lengthening the N-alkyl chain converts compounds from potent nonselective releasers showing abuse-related effects to more selective SERT releasers with no apparent abuse potential.
Keywords: ICSS; Mephedrone; amphetamine; bath salts; dopamine transporter (DAT); drug abuse; norepinephrine transporter (NET); serotonin transporter (SERT); synthetic cathinones.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
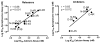

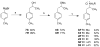
References
-
- Baumann MH, Glennon RA, Wiley JL, editors. Neuropharmacology of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS); The Science Behind the Headlines. Springer International; 2017.
-
- Gelvin EP, McGavack TH. 2-Amino-1-(p-methylphenyl)-propane (aptrol) as an anorexigenic agent in weight reduction. N Y State J Med. 1952;52:223–226. - PubMed
-
- Blanckaert P, van Amsterdam J, Brunt T, van den Berg J, Van Durme F, Maudens K, van Bussel J. 4-Methyl-amphetamine: a health threat for recreational amphetamine users. J Psychopharmacol. 2013;27:817–822. - PubMed
-
- EMCDDA. Europol Joint Report on a new psychoactive substance: 4-methylamphetamine. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

