Fibroblast growth factor 20 is protective towards dopaminergic neurons in vivo in a paracrine manner
- PMID: 29698669
- PMCID: PMC6063078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.04.017
Fibroblast growth factor 20 is protective towards dopaminergic neurons in vivo in a paracrine manner
Abstract
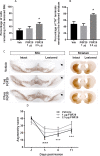
Neuroprotective strategies are an unmet medical need for Parkinson's disease. Fibroblast growth factor 20 (FGF20) enhances survival of cultured dopaminergic neurons but little is known about its in vivo potential. We set out to examine whether manipulation of the FGF20 system affected nigrostriatal tract integrity in rats, to identify which fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) might reside on dopaminergic neurons and to discover the source of endogenous FGF20 in the substantia nigra (SN). Male Sprague Dawley rats were subject to a partial 6-OHDA lesion alongside treatment with exogenous FGF20 or an FGFR antagonist. Behavioural readouts and tyrosine-hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemistry were used to evaluate nigrostriatal tract integrity. Fluorescent immunohistochemistry was used to examine FGFR subtype expression on TH-positive dopamine neurons and FGF20 cellular localisation within the SN. FGF20 (2.5 μg/day) significantly protected TH-positive cells in the SN and terminals in the striatum, while reducing the development of motor asymmetry at 5, 8 and 11 days post lesion. Conversely, the FGFR antagonist PD173074 (2 mg/kg) significantly worsened both the 6-OHDA lesion and resultant motor asymmetry. Within the SN, TH-positive cells expressed FGFR1, 3 and 4 while FGF20 co-localised with GFAP-positive astrocytes. In conclusion, FGF20 protects dopaminergic neurons in vivo, an action likely mediated through activation of FGFRs1, 3 or 4 found on these neurons. Given FGF20 is localised to astrocytes in the adult SN, endogenous FGF20 provides its protection of dopamine neurons through a paracrine action. Boosting the endogenous FGF20 production might offer potential as a future therapeutic strategy in Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: 6-Hydroxydopamine; Fibroblast growth factor 20; Fibroblast growth factor receptor; Neuroprotection; Parkinson's disease.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor-20 protects against dopamine neuron loss in vitro and provides functional protection in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Dec;63(7):1268-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.07.029. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22971544
-
Small molecule TrkB agonist deoxygedunin protects nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons from 6-OHDA and MPTP induced neurotoxicity in rodents.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:448-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.016. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26282118
-
Characterization of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, in rat partial and full nigral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion models of Parkinson's disease.Brain Res. 2016 Sep 1;1646:354-365. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.038. Epub 2016 May 24. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27233809
-
Rosiglitazone, a PPAR-γ agonist, protects against striatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by 6-OHDA lesions in the substantia nigra of rats.Toxicol Lett. 2012 Sep 18;213(3):332-44. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.07.016. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Toxicol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22842585
-
The Kv7/KCNQ channel blocker XE991 protects nigral dopaminergic neurons in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2018 Mar;137:132-139. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.11.011. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 29174294
Cited by
-
Autophagy Activation Is Involved in Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor Ameliorating Parkinson's Disease via Regulating Tribbles Homologue 3.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 2;10:1428. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01428. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849673 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 Protects Dopaminergic Neurons in Parkinson's Disease Models Via Repression of Neuroinflammation.Neurotox Res. 2020 Mar;37(3):616-627. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00151-6. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31997152
-
Cocaine induces paradigm-specific changes to the transcriptome within the ventral tegmental area.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Sep;46(10):1768-1779. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01031-4. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34155331 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 20 attenuates pathological cardiac hypertrophy by activating the SIRT1 signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Mar 28;13(3):276. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04724-w. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35351862 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of fibroblast growth factors in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1413-1427. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06890-0. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34731369 Review.
References
-
- Belluardo N., Wu G., Mudo G., Hansson A.C., Pettersson R., Fuxe K. Comparative localization of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1, -2, and -3 mRNAs in the rat brain: in situ hybridization analysis. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997;379:226–246. - PubMed
-
- Chadashvili T., Peterson D.A. Cytoarchitecture of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR-2) immunoreactivity in astrocytes of neurogenic and non-neurogenic regions of the young adult and aged rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006;498:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Chadi G., Silva C., Maximino J.R., Fuxe K., da Silva G.O. Adrenalectomy counteracts the local modulation of astroglial fibroblast growth factor system without interfering with the pattern of 6-OHDA-induced dopamine degeneration in regions of the ventral midbrain. Brain Res. 2008;1190:23–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

