Epigenomics: Technologies and Applications
- PMID: 29700067
- PMCID: PMC5929475
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.310998
Epigenomics: Technologies and Applications
Abstract
The advent of high-throughput epigenome mapping technologies has ushered in a new era of multiomics where powerful tools can now delineate and record different layers of genomic output. Integrating various components of the epigenome from these multiomics measurements allows the interrogation of cellular heterogeneity in addition to the discovery of molecular connectivity maps between the genome and its functional output. Mapping of chromatin accessibility dynamics and higher-order chromatin structure has enabled new levels of understanding of cell fate decisions, identity, and function in normal development, physiology, and disease. We provide a perspective on the progress of the epigenomics field and applications and anticipate an even greater revolution in our understanding of the human epigenome for years to come.
Keywords: chromatin; epigenomics; genomics; humans.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
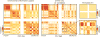
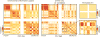

References
-
- Waddington CH. The epigenotype. 1942. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41:10–13. - PubMed
-
- Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 2004;429:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Fischle W, Cheung W, Jacobs S, Khorasanizadeh S, Allis CD. Beyond the double helix: writing and reading the histone code. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:3–17. discussion 17–21– 163–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Adli M, Zou JY, Verstappen G, Coyne M, Zhang X, Durham T, Miri M, Deshpande V, De Jager PL, Bennett DA, Houmard JA, Muoio DM, Onder TT, Camahort R, Cowan CA, Meissner A, Epstein CB, Shoresh N, Bernstein BE. Genome-wide chromatin state transitions associated with developmental and environmental cues. Cell. 2013;152:642–654. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

