Silencing SUMO2 promotes protection against degradation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through p53 signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration
- PMID: 29700214
- PMCID: PMC6023941
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171523
Silencing SUMO2 promotes protection against degradation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through p53 signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Silencing SUMO2 promotes protection against degradation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through p53 signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration.Biosci Rep. 2021 Oct 29;41(10):BSR-20171523_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20171523_RET. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34612481 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Silencing SUMO2 promotes protection against degradation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through p53 signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration.Biosci Rep. 2020 Aug 28;40(8):BSR-20171523_EOC. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20171523_EOC. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32857153 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD), as a common cause of back pain, is related to the promotion of cellular senescence and reduction in proliferation. Based on recent studies, small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) proteins have been implicated in various biological functions. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the effects of SUMO2 on proliferation and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) via mediation of p53 signaling pathway in rat models of IDD.
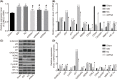
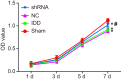
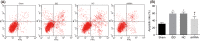
Methods: After the establishment of rat models of IDD for the measurement of positive expression of SUMO2/3 protein, the mRNA and protein levels of SUMO2, molecular phenotype [matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)] and p53 signaling pathway-related genes [p21, murine double minute-2 (MDM2), growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible protein 45 α (GADD45α), cyclin-dependent kinase 2/4 (CDK2/4), and CyclinB1] were determined, followed by the detection of cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and cell senescence.
Results: The rat models of IDD were successfully constructed. The results obtained showed that there was a higher positive expression of SUMO2/3 protein in IDD rats. Moreover, the silencing of the SUMO2 gene decreases the levels of SUMO2, p53, p21, MDM2, GADD45α, MMP-2, and HIF-1α expressions and p53 phosphorylation level while it increases the levels of CDK2/4 and CyclinB1 expressions. In addition, SUMO2 gene silencing enhances proliferation and suppresses apoptosis and cell senescence of NPCs.
Conclusion: In conclusion, SUMO2 gene silencing promotes proliferation, and inhibits the apoptosis and senescence of NPCs in rats with IDD through the down-regulation of the p53 signaling pathway. Thus, SUMO2 is a potential target in the treatment of IDD.
Keywords: Intervertebral disc degeneration; Nucleus pulposus cells; Proliferation; SUMO2 gene silencing; p53 signaling pathway.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

