Simulating SIR processes on networks using weighted shortest paths
- PMID: 29700314
- PMCID: PMC5920074
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24648-w
Simulating SIR processes on networks using weighted shortest paths
Abstract
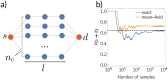
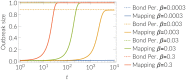
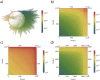
We present a framework to simulate SIR processes on networks using weighted shortest paths. Our framework maps the SIR dynamics to weights assigned to the edges of the network, which can be done for Markovian and non-Markovian processes alike. The weights represent the propagation time between the adjacent nodes for a particular realization. We simulate the dynamics by constructing an ensemble of such realizations, which can be done by using a Markov Chain Monte Carlo method or by direct sampling. The former provides a runtime advantage when realizations from all possible sources are computed as the weighted shortest paths can be re-calculated more efficiently. We apply our framework to three empirical networks and analyze the expected propagation time between all pairs of nodes. Furthermore, we have employed our framework to perform efficient source detection and to improve strategies for time-critical vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

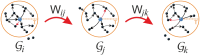

Similar articles
-
Path ensembles and path sampling in nonequilibrium stochastic systems.J Chem Phys. 2007 Sep 14;127(10):104103. doi: 10.1063/1.2775439. J Chem Phys. 2007. PMID: 17867733
-
Shortest path based network analysis to characterize cognitive load states of human brain using EEG based functional brain networks.J Integr Neurosci. 2018;17(2):133-148. doi: 10.31083/JIN-170049. J Integr Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28968248
-
Ecological networks: Pursuing the shortest path, however narrow and crooked.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 28;9(1):17826. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54206-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31780703 Free PMC article.
-
Range-limited centrality measures in complex networks.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2012 Jun;85(6 Pt 2):066103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.85.066103. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2012. PMID: 23005158
-
Estimation and update of betweenness centrality with progressive algorithm and shortest paths approximation.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 10;13(1):17110. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44392-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37816806 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
On some fundamental challenges in monitoring epidemics.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2022 Jan 10;380(2214):20210117. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2021.0117. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2022. PMID: 34802270 Free PMC article.
-
Minimizing the Spread of Negative Influence in SNIR Model by Contact Blocking.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;24(11):1623. doi: 10.3390/e24111623. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359713 Free PMC article.
-
The social dynamics of COVID-19.Physica A. 2021 Apr 1;567:125710. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2020.125710. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Physica A. 2021. PMID: 33879957 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix-Based Formulation of Heterogeneous Individual-Based Models of Infectious Diseases: Using SARS Epidemic as a Case Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 26;18(11):5716. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115716. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34073465 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 spread algorithm in the international airport network-DetArpds.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023 Feb 16;9:e1228. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1228. eCollection 2023. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 37346519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guille A, Hacid H, Favre C, Zighed DA. Information diffusion in online social networks. ACM SIGMOD Record. 2013;42:17. doi: 10.1145/2503792.2503797. - DOI
-
- Lerman, K. & Ghosh, R. Information contagion: an empirical study of the spread of news on digg and twitter social networks. In in Proc. 4th Int. Conf. on Weblogs and Social Media (ICWSM), 2010.
-
- Anderson, R. M. & May, R. M. Infectious Diseases in Humans (Oxford University Press, 1992).
-
- Vespignani A. Modelling dynamical processes in complex socio-technical systems. Nature Physics. 2011;8:32–39. doi: 10.1038/nphys2160. - DOI
-
- Pastor-Satorras R, Castellano C, Van Mieghem P, Vespignani A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015;87:925–979. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.87.925. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

