Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Presenting as a Pulsatile Neck Mass: a Case Report and Review of Literature
- PMID: 29700788
- PMCID: PMC6025654
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-018-4445-3
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Presenting as a Pulsatile Neck Mass: a Case Report and Review of Literature
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Presenting as a Pulsatile Neck Mass: a Case Report and Review of Literature.J Gen Intern Med. 2018 Dec;33(12):2257. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4692-3. J Gen Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 30306380 Free PMC article.
Abstract
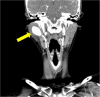
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome refers to a spectrum of connective tissue disorders typically caused by mutations in genes responsible for the synthesis of collagen. Patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome often exhibit hyperflexibility of joints, increased skin elasticity, and tissue fragility. Vascular Ehlers-Danlos (vEDS) is a subtype of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with a predilection to involve blood vessels. As such, it often manifests as vascular aneurysms and vessel rupture leading to hemorrhage. There are few reports describing primary prevention of aneurysms in the setting of undiagnosed, suspected vEDS. We present a case of a 30-year-old woman who presents with a pulsatile neck mass found to have multiple arterial aneurysms on imaging, hyperflexibility, and characteristic facial features consistent with vEDS. As described in this case, management of a suspected connective tissue disorder is a multidisciplinary approach including vascular surgery, medical therapy, and genetic testing to confirm the diagnosis. We review literature regarding the care of patients with vascular Ehlers-Danlos as it might pertain to hospitalized patients.
Keywords: Ehlers-danlos; aneurysm; vascular.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have a conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a rare disorder presenting with focal convulsions.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014 Nov;24 Suppl 3:S262-4. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014. PMID: 25518796
-
Vascular type Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome with fatal spontaneous rupture of a right common iliac artery dissection: case report and review of literature.J Radiol Case Rep. 2014 Feb 1;8(2):63-9. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v8i2.1568. eCollection 2014 Feb. J Radiol Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 24967021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multi-institutional experience in the aortic and arterial pathology in individuals with genetically confirmed vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.J Vasc Surg. 2019 Nov;70(5):1543-1554. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2019.01.069. Epub 2019 May 21. J Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31126764 Free PMC article.
-
Fulminant myocardial bleeding: another clinical course of vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.BMJ Case Rep. 2017 Sep 23;2017:bcr2017220786. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-220786. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28942401 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome With a Novel Missense COL3A1 Mutation Present With Pulmonary Complications and Iliac Arterial Dissection.Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2018 Feb;52(2):138-142. doi: 10.1177/1538574417745432. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2018. PMID: 29216800 Review.
References
-
- Barabas AP. Vascular complications in the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, with especial reference to the “arterial type” or Sack’s syndrome. J Cardiovasc Surg. 1972;13:160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

