Identification of novel circulatory microRNA signatures linked to patients with ischemic stroke
- PMID: 29701837
- PMCID: PMC6005038
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy136
Identification of novel circulatory microRNA signatures linked to patients with ischemic stroke
Abstract
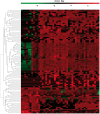
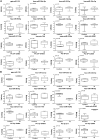
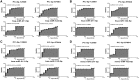
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in growth, development, and occurrence and progression of many diseases. MiRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation is poorly understood in vascular biology and pathology. The purpose of this is to determine circulatory miRNAs as early detectable peripheral biomarkers in patients with ischemic stroke (IS). MiRNAs expression levels were measured in IS serum samples and healthy controls using Illumina deep sequencing analysis and identified differentially expressed miRNAs. Differentially expressed miRNAs were further validated using SYBR-green-based quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) assay in postmortem IS brains, lymphoblastoid IS cell lines, oxygen and glucose deprivation/reoxygenation -treated human and mouse neuroblastoma cells, and mouse models of hypoxia and ischemia (HI)-induced stroke. A total of 4656 miRNAs were differentially expressed in IS serum samples relative to healthy controls. Out of 4656 miRNAs, 272 were found to be significantly deregulated in IS patients. Interestingly, we found several novel and previously unreported miRNAs in IS patients relative to healthy controls. Further analyses revealed that some candidate miRNAs and its target genes were involved in the regulation of the stroke. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study identified potential novel candidate miRNAs in IS serum samples from the residents of rural West Texas. MiRNAs identified in this study could potentially be used as a biomarker and the development of novel therapeutic approaches for stroke. Further studies are necessary to better understand miRNAs-regulated stroke cellular changes.
Figures



References
-
- Lozano R., Naghavi M., Foreman K., Lim S., Shibuya K., Aboyans V., Abraham J., Adair T., Aggarwal R., Ahn S.Y.. et al. (2012) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet, 380, 2095–2128. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murray C.J., Vos T., Lozano R., Naghavi M., Flaxman A.D., Michaud C., Ezzati M., Shibuya K., Salomon J.A., Abdalla S.. et al. (2012) Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet, 380, 2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin E.J., Blaha M.J., Chiuve S.E., Cushman M., Das S.R., Deo R., de Ferranti S.D., Floyd J., Fornage M., Gillespie C.. et al. (2017) American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 135, e146–e603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W., Flegal K., Furie K., Go A., Greenlund K., Haase N., Hailpern S.M., Ho M., Howard V., Kissela B.. et al. (2008) American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation, 117, e25–e146. - PubMed
-
- Pendlebury S.T., Rothwell P.M. (2009) Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol., 8, 1006–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

