Optical Detection of Ketoprofen by Its Electropolymerization on an Indium Tin Oxide-Coated Optical Fiber Probe
- PMID: 29702595
- PMCID: PMC5982105
- DOI: 10.3390/s18051361
Optical Detection of Ketoprofen by Its Electropolymerization on an Indium Tin Oxide-Coated Optical Fiber Probe
Abstract
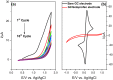
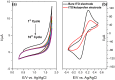
In this work an application of optical fiber sensors for real-time optical monitoring of electrochemical deposition of ketoprofen during its anodic oxidation is discussed. The sensors were fabricated by reactive magnetron sputtering of indium tin oxide (ITO) on a 2.5 cm-long core of polymer-clad silica fibers. ITO tuned in optical properties and thickness allows for achieving a lossy-mode resonance (LMR) phenomenon and it can be simultaneously applied as an electrode in an electrochemical setup. The ITO-LMR electrode allows for optical monitoring of changes occurring at the electrode during electrochemical processing. The studies have shown that the ITO-LMR sensor’s spectral response strongly depends on electrochemical modification of its surface by ketoprofen. The effect can be applied for real-time detection of ketoprofen. The obtained sensitivities reached over 1400 nm/M (nm·mg−1·L) and 16,400 a.u./M (a.u.·mg−1·L) for resonance wavelength and transmission shifts, respectively. The proposed method is a valuable alternative for the analysis of ketoprofen within the concentration range of 0.25⁻250 μg mL−1, and allows for its determination at therapeutic and toxic levels. The proposed novel sensing approach provides a promising strategy for both optical and electrochemical detection of electrochemical modifications of ITO or its surface by various compounds.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory drug; drug analysis; electrochemistry; electropolymerization; indium tin oxide (ITO); ketoprofen; lossy-mode resonance (LMR); optical fiber sensor; reactive magnetron sputtering thin film.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Asanuma M., Asanuma S.N., Gómez-Vargas M., Yamamoto M., Ogawa N. Ketoprofen, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug prevents the late-onset reduction of muscarinic receptors in gerbil hippocampus after transient forebrain ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 1997;225:109–112. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(97)00204-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patrolecco L., Ademollo N., Grenni P., Tolomei A., Barra Caracciolo A., Capri S. Simultaneous determination of human pharmaceuticals in water samples by solid phase extraction and HPLC with UV-fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2013;107:165–171. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2012.05.035. - DOI
-
- Muhammad N., Li W., Subhani Q., Wang F., Zhao Y.-G., Zhu Y. Dual application of synthesized SnO2 nanoparticles in ion chromatography for sensitive fluorescence determination of ketoprofen in human serum, urine, and canal water samples. New J. Chem. 2017;41:9321–9329. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ01757J. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

