SMAD4 and NF1 mutations as potential biomarkers for poor prognosis to cetuximab-based therapy in Chinese metastatic colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 29703253
- PMCID: PMC5921972
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4298-5
SMAD4 and NF1 mutations as potential biomarkers for poor prognosis to cetuximab-based therapy in Chinese metastatic colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Cetuximab, an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, is used in combination with chemotherapy in clinic to enhance the outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients with only ~ 20% response rate. To date only activating mutations in KRAS and NRAS have been identified as poor prognosis biomarkers in cetuximab-based treatment, which makes an urgent need for identification of novel prognosis biomarkers to precisely predict patients' response in order to maximize the benefit.
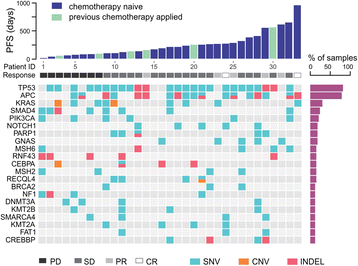
Methods: In this study, we analysed the mutation profiles of 33 Chinese mCRC patients using comprehensive next-generation sequencing (NGS) targeting 416 cancer-relevant genes before cetuximab treatment. Upon receiving cetuximab-based therapy, patients were evaluated for drug response, and the progression-free survival (PFS) was monitored. The association of specific genetic alterations and cetuximab efficacy was analyzed.
Results: Patients carrying SMAD4 mutations (SMAD4mut, n = 8) or NF1 mutations (NF1mut, n = 4) had significantly shorter PFS comparing to those carrying wildtype SMAD4 (SMAD4wt, n = 25) (P = 0.0081) or wildtype NF1 (NF1wt, n = 29) (P = 0.0028), respectively. None of the SMAD4mut or NF1mut patients showed response to cetuximab when assessed at 12-week post-treatment. Interestingly, two patients carrying both SMAD4mut and NF1mut showed the shortest PFS among all the patients.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrated that SMAD4 and NF1 mutations can serve as potential biomarkers for poor prognosis to cetuximab-based therapy in Chinese mCRC patients.
Keywords: Cetuximab; Metastatic colorectal cancer; NF1; Next-generation sequencing; Prognosis; SMAD4.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethic committee of the First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University. All the patients enrolled in this study have provided written informed consents for specimen collection, genetic testing, and participation in the research anonymously.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Yang W. Shao, Yan Ding, Xiangyuan Ma, and Xue Wu are the shareholders or employees of Geneseeq Technology Inc.; Yewei Xia, and Dongqin Zhu are the employee of Nanjing Geneseeq Technology Inc..
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

