Rationale and Design of the CONCERT-HF Trial (Combination of Mesenchymal and c-kit+ Cardiac Stem Cells As Regenerative Therapy for Heart Failure)
- PMID: 29703749
- PMCID: PMC5993622
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312978
Rationale and Design of the CONCERT-HF Trial (Combination of Mesenchymal and c-kit+ Cardiac Stem Cells As Regenerative Therapy for Heart Failure)
Abstract
Rationale: Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and c-kit+ cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) are 2 promising cell types being evaluated for patients with heart failure (HF) secondary to ischemic cardiomyopathy. No information is available in humans about the relative efficacy of MSCs and CPCs and whether their combination is more efficacious than either cell type alone.
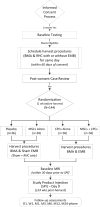
Objective: CONCERT-HF (Combination of Mesenchymal and c-kit+ Cardiac Stem Cells As Regenerative Therapy for Heart Failure) is a phase II trial aimed at elucidating these issues by assessing the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of transendocardial administration of autologous MSCs and CPCs, alone and in combination, in patients with HF caused by chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy (coronary artery disease and old myocardial infarction).
Methods and results: Using a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multicenter, multitreatment, and adaptive design, CONCERT-HF examines whether administration of MSCs alone, CPCs alone, or MSCs+CPCs in this population alleviates left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction, reduces scar size, improves quality of life, or augments functional capacity. The 4-arm design enables comparisons of MSCs alone with CPCs alone and with their combination. CONCERT-HF consists of 162 patients, 18 in a safety lead-in phase (stage 1) and 144 in the main trial (stage 2). Stage 1 is complete, and stage 2 is currently randomizing patients from 7 centers across the United States.
Conclusions: CONCERT-HF will provide important insights into the potential therapeutic utility of MSCs and CPCs, given alone and in combination, for patients with HF secondary to ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT02501811.
Keywords: cell-based therapy; clinical trial; coronary artery disease; heart failure.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
References
-
- Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, He H, Rezvani M, Ingwall JS, Dzau VJ. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with akt prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 2003;9:1195–1201. - PubMed
-
- Hatzistergos KE, Quevedo H, Oskouei BN, Hu Q, Feigenbaum GS, Margitich IS, Mazhari R, Boyle AJ, Zambrano JP, Rodriguez JE, Dulce R, Pattany PM, Valdes D, Revilla C, Heldman AW, McNiece I, Hare JM. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells stimulate cardiac stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Circ Res. 2010;107:913–922. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shake JG, Gruber PJ, Baumgartner WA, Senechal G, Meyers J, Redmond JM, Pittenger MF, Martin BJ. Mesenchymal stem cell implantation in a swine myocardial infarct model: Engraftment and functional effects. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73:1919–25. discussion 1926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous