Brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine: a highly active first salvage regimen for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 29703778
- PMCID: PMC6073588
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-815183
Brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine: a highly active first salvage regimen for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is standard of care for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) who have relapsed/refractory disease after frontline chemotherapy. Achievement of complete remission (CR) with pre-ASCT salvage chemotherapy predicts favorable outcomes post-ASCT. This phase 1/2 study evaluated the combination of brentuximab vedotin (BV) plus bendamustine as a first salvage regimen in relapsed/refractory HL. A total of 55 patients (28 primary refractory and 27 relapsed) were enrolled. Patients received BV (1.8 mg/kg) on day 1 and bendamustine (90 mg/m2) on days 1 and 2 of a 21-day cycle for up to 6 cycles. Patients could undergo ASCT any time after cycle 2. Following ASCT or completion of combination therapy if not proceeding to ASCT, patients could receive BV monotherapy for up to 16 cycles of total therapy. After a median of 2 cycles of combination therapy (range, 1-6), the objective response rate among 53 efficacy-evaluable patients was 92.5%, with 39 patients (73.6%) achieving CR. Forty patients underwent ASCT. Thirty-one patients (25 of whom underwent ASCT) received BV monotherapy (median, 10 cycles; range, 1-14). After a median of 20.9 months of follow-up, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival was 69.8% and 62.6% for patients who received ASCT and all patients, respectively. Thirty-one patients (56.4%) experienced infusion-related reactions (IRRs), with a majority occurring during cycle 2 of combination therapy. A protocol amendment requiring premedication reduced IRR severity. BV plus bendamustine as first salvage therapy in relapsed/refractory HL is highly active with a manageable toxicity profile. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01874054.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The institutions of A.S.L., R.G.B., A.S., P.C., E.A., J.M., S.M.A., H.E.C., M.I.-O., C.B., E.C., A.F.-T., J.V., O.A.O., and R.A. received funding from Seattle Genetics, Inc. to conduct the trial. H.E.C. and N.J. have equity ownership in Seattle Genetics, Inc. J.V. and A.S. have received honoraria from Seattle Genetics, Inc. J.M. and C.B. have participated in a speakers’ bureau for Seattle Genetics, Inc and Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc, a wholly owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceuticals Limited. O.A.O. has received research funding from Seattle Genetics, Inc. H.E.C. has acted as a consultant for and has received travel expenses from Seattle Genetics, Inc. N.J. and Y.W. are employed by Seattle Genetics, Inc.
Figures
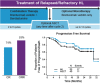


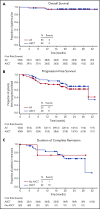

Comment in
-
Getting to transplant in Hodgkin lymphoma: BVB.Blood. 2018 Jul 5;132(1):1-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-848366. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29976776 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gordon LI, Hong F, Fisher RI, et al. Randomized phase III trial of ABVD versus Stanford V with or without radiation therapy in locally extensive and advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma: an intergroup study coordinated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (E2496). J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(6):684-691. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moskowitz CH, Nimer SD, Zelenetz AD, et al. A 2-step comprehensive high-dose chemoradiotherapy second-line program for relapsed and refractory Hodgkin disease: analysis by intent to treat and development of a prognostic model. Blood. 2001;97(3):616-623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

