Simultaneous sequencing of coding and noncoding RNA reveals a human transcriptome dominated by a small number of highly expressed noncoding genes
- PMID: 29703781
- PMCID: PMC6004057
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.064493.117
Simultaneous sequencing of coding and noncoding RNA reveals a human transcriptome dominated by a small number of highly expressed noncoding genes
Abstract
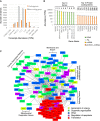
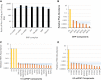
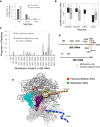
Comparing the abundance of one RNA molecule to another is crucial for understanding cellular functions but most sequencing techniques can target only specific subsets of RNA. In this study, we used a new fragmented ribodepleted TGIRT sequencing method that uses a thermostable group II intron reverse transcriptase (TGIRT) to generate a portrait of the human transcriptome depicting the quantitative relationship of all classes of nonribosomal RNA longer than 60 nt. Comparison between different sequencing methods indicated that FRT is more accurate in ranking both mRNA and noncoding RNA than viral reverse transcriptase-based sequencing methods, even those that specifically target these species. Measurements of RNA abundance in different cell lines using this method correlate with biochemical estimates, confirming tRNA as the most abundant nonribosomal RNA biotype. However, the single most abundant transcript is 7SL RNA, a component of the signal recognition particle.
Keywords: RNA detection; high-throughput sequencing; noncoding RNA; snoRNA; thermostable group II intron reverse transcriptase; transcriptome analysis.
© 2018 Boivin et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures


References
-
- Bai B, Laiho M. 2016. Deep sequencing analysis of nucleolar small RNAs: RNA isolation and library preparation. Methods Mol Biol 1455: 231–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
