A kindred with mutant IKAROS and autoimmunity
- PMID: 29705243
- PMCID: PMC6541477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.04.008
A kindred with mutant IKAROS and autoimmunity
Abstract
IKAROS (encoded by IKZF1) is an important hematopoietic transcription factor critical for early B cell differentiation, with major defects known to lead to low B cell numbers and hypogammaglobulinemia. More perplexing is the link between IKZF1 variants and autoimmunity, including polymorphisms associated with susceptibility to SLE, and recently, rare variants driving monogenic autoimmunity. We identified a novel p.L188V mutation in IKZF1 in the index patient and her father and found this mutation to lead to loss of DNA binding. Peripheral B cells lacking a full complement of IKAROS function show upregulation of molecules accentuating B cell activation, while CD22, a key negative feedback circuit, is suppressed. The resulting hyperresponsiveness of peripheral B cells, in combination with elevated follicular helper T cell (Tfh) numbers, provides a putative mechanistic explanation for the association of IKZF1 variants with the emergence of autoimmune manifestations in this kindred.
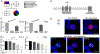
Figures

References
-
- Georgopoulos K, Winandy S, Avitahl N. The role of the Ikaros gene in lymphocyte development and homeostasis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997; 15(1): 155–176. - PubMed
-
- Kirstetter P, Thomas M, Dierich A, Kastner P, Chan S. Ikaros is critical for B cell differentiation and function. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32(3):720–730. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino A, Okada S, Yoshida K, Nishida N, Okuno Y, Ueno H, et al. Abnormal hematopoiesis and autoimmunity in human subjects with germline IKZF1 mutations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

