The Impact of Pazopanib on the Cardiovascular System
- PMID: 29706106
- PMCID: PMC6257996
- DOI: 10.1177/1074248418769612
The Impact of Pazopanib on the Cardiovascular System
Abstract
Pazopanib is an approved treatment for renal cell carcinoma and a second-line treatment for nonadipocytic soft-tissue sarcoma. However, its clinical efficacy is limited by its cardiovascular side effects. Pazopanib and other vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been associated with the development of hypertension, QT interval prolongation, and other cardiovascular events; however, these mechanisms are largely unknown. Gaining a deeper understanding of these mechanisms is essential for the development of appropriate surveillance strategies and possible diagnostic biomarkers to allow us to monitor patients and modulate therapy prior to significant cardiac insult. This approach will be vital in keeping patients on these life-saving therapies and may be applicable to other tyrosine kinase inhibitors as well. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the preclinical and clinical side effects of pazopanib with a focus on the mechanisms responsible for its toxicity to the cardiovascular system.
Keywords: hypertension; pazopanib; renal cell carcinoma; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
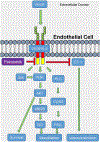
Figures

References
-
- Znaor A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Laversanne M, Jemal A, Bray F. International variations and trends in renal cell carcinoma incidence and mortality. Eur Urol. 2015;67(3):519–530. - PubMed
-
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome. 2017. https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/birt-hogg-dubé-syndrome. Accessed November 27, 2017.
-
- Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(5):1011–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

