Monoallelic Mutations to DNAJB11 Cause Atypical Autosomal-Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 29706351
- PMCID: PMC5986722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.03.013
Monoallelic Mutations to DNAJB11 Cause Atypical Autosomal-Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abstract
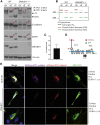
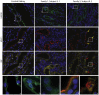
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is characterized by the progressive development of kidney cysts, often resulting in end-stage renal disease (ESRD). This disorder is genetically heterogeneous with ∼7% of families genetically unresolved. We performed whole-exome sequencing (WES) in two multiplex ADPKD-like pedigrees, and we analyzed a further 591 genetically unresolved, phenotypically similar families by targeted next-generation sequencing of 65 candidate genes. WES identified a DNAJB11 missense variant (p.Pro54Arg) in two family members presenting with non-enlarged polycystic kidneys and a frameshifting change (c.166_167insTT) in a second family with small renal and liver cysts. DNAJB11 is a co-factor of BiP, a key chaperone in the endoplasmic reticulum controlling folding, trafficking, and degradation of secreted and membrane proteins. Five additional multigenerational families carrying DNAJB11 mutations were identified by the targeted analysis. The clinical phenotype was consistent in the 23 affected members, with non-enlarged cystic kidneys that often evolved to kidney atrophy; 7 subjects reached ESRD from 59 to 89 years. The lack of kidney enlargement, histologically evident interstitial fibrosis in non-cystic parenchyma, and recurring episodes of gout (one family) suggested partial phenotypic overlap with autosomal-dominant tubulointerstitial diseases (ADTKD). Characterization of DNAJB11-null cells and kidney samples from affected individuals revealed a pathogenesis associated with maturation and trafficking defects involving the ADPKD protein, PC1, and ADTKD proteins, such as UMOD. DNAJB11-associated disease is a phenotypic hybrid of ADPKD and ADTKD, characterized by normal-sized cystic kidneys and progressive interstitial fibrosis resulting in late-onset ESRD.
Keywords: ADPKD; ADPLD; ADTKD; DNAJB11; pathogenic variants; renal cystic disease.
Copyright © 2018 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
DNAJB11: another player in ADPKD.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018 Aug;14(8):476. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0024-4. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29777155 No abstract available.
-
DNAJB11 Mutation in ADPKD Patients: Clinical Characteristics in a Monocentric Cohort.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 19;15(1):3. doi: 10.3390/genes15010003. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong A.C., Devuyst O., Knebelmann B., Walz G., Diseases, ERA-EDTA Working Group for Inherited Kidney Diseases Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the changing face of clinical management. Lancet. 2015;385:1993–2002. - PubMed
-
- The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell. 1994;77:881–894. - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki T., Wu G., Hayashi T., Xenophontos S.L., Veldhuisen B., Saris J.J., Reynolds D.M., Cai Y., Gabow P.A., Pierides A. PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes an integral membrane protein. Science. 1996;272:1339–1342. - PubMed
-
- Heyer C.M., Sundsbak J.L., Abebe K.Z., Chapman A.B., Torres V.E., Grantham J.J., Bae K.T., Schrier R.W., Perrone R.D., Braun W.E., HALT PKD and CRISP Investigators Predicted mutation strength of nontruncating PKD1 mutations aids genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016;27:2872–2884. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK062401/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113111/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056956/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062402/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079310/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK106912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062408/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062411/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062410/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK090728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018521/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007276/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

