The Effect of Resection Angle on Stress Distribution after Root-End Surgery
- PMID: 29707013
- PMCID: PMC5911292
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v13i2.19089
The Effect of Resection Angle on Stress Distribution after Root-End Surgery
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to investigate the influence of the resection angle on the stress distribution of retrograde endodontic treated maxillary incisors under oblique-load application.
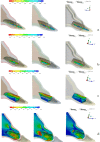
Methods and materials: A maxillary central incisor which was endodontically treated and restored with a fiber glass post was obtained in a 3-dimensional numerical model and distributed into three groups according to type of resection: control; restored with fiber post without retrograde obturation, R45 and R90 with 45º and 90º resection from tooth axial axis, respectively and restored with Fuji II LC (GC America). The numerical models received a 45º occlusal load of 200 N/cm2 on the middle of lingual surface. All materials and structures were considered linear elastic, homogeneous and isotropic. Numerical models were plotted and meshed with isoparametric elements, and the results were analyzed using maximum principal stress (MPS).
Results: MPS showed greater stress values in the bone tissue for control group than the other groups. Groups with apicectomy showed acceptable stress distribution on the fiber post, cement layer and root dentin, presenting more improved values than control group.
Conclusion: Apicectomy at 90º promotes more homogeneity on stress distribution on the fiber post, cement layer and root dentin, which suggests less probability of failure. However, due to its facility and stress distribution also being better than control group, apicectomy at 45° could be a good choice for clinicians.
Keywords: Apicectomy; Cut Angle; Dental Stress Analysis; Endodontics; Finite Element Analysis; Resection Angle.
Conflict of interest statement
‘None declared’.
Figures


References
-
- Song M, Kim SG, Shin SJ, Kim HC, Kim E. The influence of bone tissue deficiency on the outcome of endodontic microsurgery: a prospective study. J Endod. 2013;39(11):1341–5. - PubMed
-
- Jang Y, Hong HT, Roh BD, Chun HJ. Influence of apical root resection on the biomechanical response of a single-rooted tooth: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J Endod. 2014;40(9):1489–93. - PubMed
-
- Garip H, Garip Y, Orucoglu H, Hatipoglu S. Effect of the angle of apical resection on apical leakage, measured with a computerized fluid filtration device. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;111(3):e50–5. - PubMed
-
- Bystrom A, Happonen RP, Sjogren U, Sundqvist G. Healing of periapical lesions of pulpless teeth after endodontic treatment with controlled asepsis. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1987;3(2):58–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
