An initial exploration for comprehensive assessment of IgG4-related lung disease: analyses on the cases enrolled from a systematic review
- PMID: 29707337
- PMCID: PMC5906340
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2018.01.149
An initial exploration for comprehensive assessment of IgG4-related lung disease: analyses on the cases enrolled from a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The existence of two diagnostic systems, the Boston and Japan criteria, for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) confuse the medical practice. We aimed to develop a comprehensive assessment based on the weight of each diagnostic item in the existing criteria to improve the diagnostic efficiency of Boston criteria.
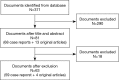
Methods: We assessed the patients enrolled by a systematic review of the literatures using the Boston criteria, Japan criteria and a tentative comprehensive assessment respectively, and evaluated the efficiency of each system and their consistency.
Results: Our analysis showed that the distinction in pathological diagnostic items was similar for the Boston criteria (IgG4+/IgG+ ratio, P<0.01; the number of pathological features and IgG4+ count, P<0.001) and comprehensive assessment (IgG4+/IgG+ ratio and the number of pathological features, P<0.001; IgG4+ count, P<0.05). For the Japan criteria, a good distinction in the number of pathological features was demonstrated (P<0.05) but the difference in the IgG4+/IgG+ ratio and IgG4+ count was not significant. There was relatively poor consistency between the Boston and Japan criteria (Kappa =0.482, P<0.001), while there was good agreement (Kappa =0.811, P<0.001), but a significant difference (P=0.011, McNemar matching test), between the Boston criteria and comprehensive assessment.
Conclusions: The current two diagnostic systems have poor consistency. Comprehensive assessment has good agreement with the Boston criteria, but can identify those cases in Boston Category 3 who could still be diagnosed as IgG4-related lung disease. Considering the weight of diagnostic items, the scoring system is a tentative exploration that should be improved with further experience in diagnosing IgG4-related lung disease.
Keywords: Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease (IgG4-RLD); diagnosis; histopathology; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
