Regulation of inflammatory mediator expression in bovine endometrial cells: effects of lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha
- PMID: 29707922
- PMCID: PMC5925570
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13676
Regulation of inflammatory mediator expression in bovine endometrial cells: effects of lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha
Abstract
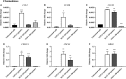
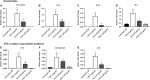
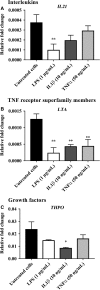
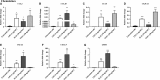
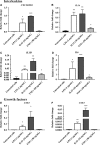
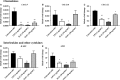
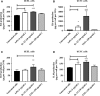
An abnormal uterine environment can influence maternal-fetal communication, conception rate and disrupt normal embryo development, thereby affecting fertility and the reproductive performance of dairy cows. Animal variability means that development of endometrial cell lines with appropriate characteristic are required. We evaluated the effect of an infectious agent (i.e., bacterial lipopolysaccharide; LPS) and proinflammatory mediators (i.e., Interleukin 1 beta; IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor alpha; TNFα) on inflammatory mediator gene expression and production by bovine endometrial epithelial (bEEL) and stromal (bCSC) cell lines. Expression of CXCL8/IL8, IL1A, IL1B, and IL6 cytokine genes was significantly upregulated in both epithelial and stromal cells when treated with LPS and IL-1β. LPS treatment of epithelial cells (compared with treatment by IL-1β and TNFα) exhibited greater CXCL8/IL8, IL1A, IL1B, and IL6 cytokine gene expression. Whereas, in stromal cells, IL-1β treatment (compared with LPS and TNFα) exhibited greater CXCL8/IL8, IL1A, IL1B, and IL6 cytokine gene expression. Interestingly, bEEL and bCSC cells treated with IL-1β increased IL1B gene expression, suggesting that IL-1β may act unusually in an autocrine-positive feedback loop. Cytokine production was stimulated by these agents in both cell types. We suggest that the characteristics of these two cell lines make them excellent tools for the study of intrauterine environment.
Keywords: Bovine; cytokines; endometrium; epithelial; stromal.
© 2018 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Acosta‐Rodriguez, E. V. , Napolitani G., Lanzavecchia A., and Sallusto F.. 2007. Interleukins 1 beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor‐beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17‐producing human T helper cells. Nat. Immunol. 8:942–949. - PubMed
-
- Arici, A. , Head J. R., MacDonald P. C., and Casey M. L.. 1993. Regulation of interleukin‐8 gene expression in human endometrial cells in culture. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 94:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Arima, K. , Nasu K., Narahara H., Fujisawa K., Matsui N., and Miyakawa I.. 2000. Effects of lipopolysaccharide and cytokines on production of RANTES by cultured human endometrial stromal cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 6:246–251. - PubMed
-
- Bahr, A. , and Wolf E.. 2012. Domestic animal models for biomedical research. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 47(Suppl 4):59–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

