Co-translational protein targeting facilitates centrosomal recruitment of PCNT during centrosome maturation in vertebrates
- PMID: 29708497
- PMCID: PMC5976437
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.34959
Co-translational protein targeting facilitates centrosomal recruitment of PCNT during centrosome maturation in vertebrates
Abstract
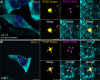
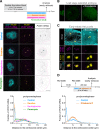
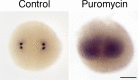
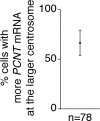
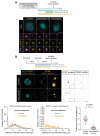
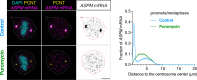
As microtubule-organizing centers of animal cells, centrosomes guide the formation of the bipolar spindle that segregates chromosomes during mitosis. At mitosis onset, centrosomes maximize microtubule-organizing activity by rapidly expanding the pericentriolar material (PCM). This process is in part driven by the large PCM protein pericentrin (PCNT), as its level increases at the PCM and helps recruit additional PCM components. However, the mechanism underlying the timely centrosomal enrichment of PCNT remains unclear. Here, we show that PCNT is delivered co-translationally to centrosomes during early mitosis by cytoplasmic dynein, as evidenced by centrosomal enrichment of PCNT mRNA, its translation near centrosomes, and requirement of intact polysomes for PCNT mRNA localization. Additionally, the microtubule minus-end regulator, ASPM, is also targeted co-translationally to mitotic spindle poles. Together, these findings suggest that co-translational targeting of cytoplasmic proteins to specific subcellular destinations may be a generalized protein targeting mechanism.
Keywords: cell biology; centrosome; human; mRNA localization; translation; zebrafish.
© 2018, Sepulveda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GS, MA, IB, KM, TO, NC, LC, LC, XJ, DY, BH, LJ No competing interests declared
Figures
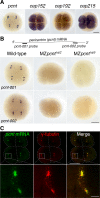

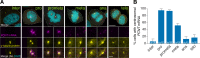

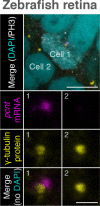


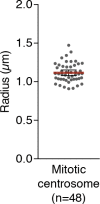



References
-
- Anitha A, Nakamura K, Yamada K, Iwayama Y, Toyota T, Takei N, Iwata Y, Suzuki K, Sekine Y, Matsuzaki H, Kawai M, Thanseem I, Miyoshi K, Katayama T, Matsuzaki S, Baba K, Honda A, Hattori T, Shimizu S, Kumamoto N, Kikuchi M, Tohyama M, Yoshikawa T, Mori N. Association studies and gene expression analyses of the DISC1-interacting molecules, pericentrin 2 (PCNT2) and DISC1-binding zinc finger protein (DBZ), with schizophrenia and with bipolar disorder. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B:967–976. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30926. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

