Autophagy: The multi-purpose bridge in viral infections and host cells
- PMID: 29709097
- PMCID: PMC7169200
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.1973
Autophagy: The multi-purpose bridge in viral infections and host cells
Abstract
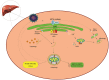
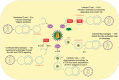
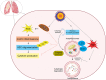
Autophagy signaling pathway is involved in cellular homeostasis, developmental processes, cellular stress responses, and immune pathways. The aim of this review is to summarize the relationship between autophagy and viruses. It is not possible to be fully comprehensive, or to provide a complete "overview of all viruses". In this review, we will focus on the interaction of autophagy and viruses and survey how human viruses exploit multiple steps in the autophagy pathway to help viral propagation and escape immune response. We discuss the role that macroautophagy plays in cells infected with hepatitis C virus, hepatitis B virus, rotavirus gastroenteritis, immune cells infected with human immunodeficiency virus, and viral respiratory tract infections both influenza virus and coronavirus.
Keywords: autophagy; host cell; interaction; virus.
Copyright © 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Cao Y, Klionsky DJ. Physiological functions of Atg6/Beclin 1: a unique autophagy‐related protein. Cell Res. 2007;17(10):839‐849. - PubMed
-
- Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self‐digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell. 2004;6(4):463‐477. - PubMed
-
- Eskelinen E‐L. Maturation of autophagic vacuoles in mammalian cells. Autophagy. 2005;1(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

