Structural Insights into N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in the Transcriptome
- PMID: 29709557
- PMCID: PMC6112310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.03.001
Structural Insights into N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in the Transcriptome
Abstract
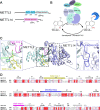
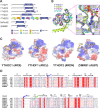
More than 100 types of chemical modifications in RNA have been well documented. Recently, several modifications, such as N6-methyladenosine (m6A), have been detected in mRNA, opening the window into the realm of epitranscriptomics. The m6A modification is the most abundant modification in mRNA and non-coding RNA (ncRNA). At the molecular level, m6A affects almost all aspects of mRNA metabolism, including splicing, translation, and stability, as well as microRNA (miRNA) maturation, playing essential roles in a range of cellular processes. The m6A modification is regulated by three classes of proteins generally referred to as the "writer" (adenosine methyltransferase), "eraser" (m6A demethylating enzyme), and "reader" (m6A-binding protein). The m6A modification is reversibly installed and removed by writers and erasers, respectively. Readers, which are members of the YT521-B homology (YTH) family proteins, selectively bind to RNA and affect its fate in an m6A-dependent manner. In this review, we summarize the structures of the functional proteins that modulate the m6A modification, and provide our insights into the m6A-mediated gene regulation.
Keywords: Epitranscriptomics; Eraser; M(6)A modification; Reader; Writer.
Copyright © 2018. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Understanding m6A Function Through Uncovering the Diversity Roles of YTH Domain-Containing Proteins.Mol Biotechnol. 2019 May;61(5):355-364. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-00149-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30637606 Review.
-
The detection and functions of RNA modification m6A based on m6A writers and erasers.J Biol Chem. 2021 Aug;297(2):100973. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100973. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34280435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YTH Domain: A Family of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Readers.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018 Apr;16(2):99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29715522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and evolution of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;16(11):1929-1940. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45231. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32398960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism.Cell Res. 2018 Jun;28(6):616-624. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8. Epub 2018 May 22. Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29789545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of m6A epigenetic modifications in tumor coding and non-coding RNA processing.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec 15;21(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01385-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38102645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The m6A-ncRNAs axis in diabetes complications: novel mechanism and therapeutic potential.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 24;15:1426380. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1426380. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38978623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VIRMA-Dependent N6-Methyladenosine Modifications Regulate the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs CCAT1 and CCAT2 in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 25;12(4):771. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040771. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32218194 Free PMC article.
-
Reading the epitranscriptome of the human malaria parasite.Biomed J. 2025 Apr;48(2):100703. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100703. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 38316392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and clinical landscape of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in gastrointestinal tract cancers.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jul;479(7):1553-1570. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05040-x. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38856795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li X., Xiong X., Yi C. Epitranscriptome sequencing technologies: decoding RNA modifications. Nat Methods. 2016;14:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D., Moshitch-Moshkovitz S., Schwartz S., Salmon-Divon M., Ungar L., Osenberg S. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

