Impact of Healthy Lifestyle Factors on Life Expectancies in the US Population
- PMID: 29712712
- PMCID: PMC6207481
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032047
Impact of Healthy Lifestyle Factors on Life Expectancies in the US Population
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Impact of Healthy Lifestyle Factors on Life Expectancies in the US Population.Circulation. 2018 Jul 24;138(4):e75. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000587. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 30571372 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Americans have a shorter life expectancy compared with residents of almost all other high-income countries. We aim to estimate the impact of lifestyle factors on premature mortality and life expectancy in the US population.
Methods: Using data from the Nurses' Health Study (1980-2014; n=78 865) and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2014, n=44 354), we defined 5 low-risk lifestyle factors as never smoking, body mass index of 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2, ≥30 min/d of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake, and a high diet quality score (upper 40%), and estimated hazard ratios for the association of total lifestyle score (0-5 scale) with mortality. We used data from the NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys; 2013-2014) to estimate the distribution of the lifestyle score and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention WONDER database to derive the age-specific death rates of Americans. We applied the life table method to estimate life expectancy by levels of the lifestyle score.
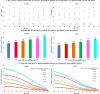
Results: During up to 34 years of follow-up, we documented 42 167 deaths. The multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios for mortality in adults with 5 compared with zero low-risk factors were 0.26 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.22-0.31) for all-cause mortality, 0.35 (95% CI, 0.27-0.45) for cancer mortality, and 0.18 (95% CI, 0.12-0.26) for cardiovascular disease mortality. The population-attributable risk of nonadherence to 5 low-risk factors was 60.7% (95% CI, 53.6-66.7) for all-cause mortality, 51.7% (95% CI, 37.1-62.9) for cancer mortality, and 71.7% (95% CI, 58.1-81.0) for cardiovascular disease mortality. We estimated that the life expectancy at age 50 years was 29.0 years (95% CI, 28.3-29.8) for women and 25.5 years (95% CI, 24.7-26.2) for men who adopted zero low-risk lifestyle factors. In contrast, for those who adopted all 5 low-risk factors, we projected a life expectancy at age 50 years of 43.1 years (95% CI, 41.3-44.9) for women and 37.6 years (95% CI, 35.8-39.4) for men. The projected life expectancy at age 50 years was on average 14.0 years (95% CI, 11.8-16.2) longer among female Americans with 5 low-risk factors compared with those with zero low-risk factors; for men, the difference was 12.2 years (95% CI, 10.1-14.2).
Conclusions: Adopting a healthy lifestyle could substantially reduce premature mortality and prolong life expectancy in US adults.
Keywords: healthy lifestyle; life expectancy; mortality, premature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Woolf SH, Aron L, editors. US Health in International Perspective: Shorter Lives, Poorer Health. Washington (DC): 2013. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization W. Global Health Observatory Data Repository: Life expectancy - Data by country. Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. [Accessed February 14, 2018]. at http://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.WOMENLEXv.
-
- World Bank. [Accessed July 12, 2017];World Development Indicators: Health systems. at http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.XPD.TOTL.ZS?year_high_desc=true.
-
- Behrens G, Fischer B, Kohler S, Park Y, Hollenbeck AR, Leitzmann MF. Healthy lifestyle behaviors and decreased risk of mortality in a large prospective study of U.S. women and men. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013;28:361–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

