The Rosa genome provides new insights into the domestication of modern roses
- PMID: 29713014
- PMCID: PMC5984618
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0110-3
The Rosa genome provides new insights into the domestication of modern roses
Abstract
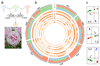
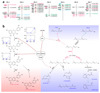
Roses have high cultural and economic importance as ornamental plants and in the perfume industry. We report the rose whole-genome sequencing and assembly and resequencing of major genotypes that contributed to rose domestication. We generated a homozygous genotype from a heterozygous diploid modern rose progenitor, Rosa chinensis 'Old Blush'. Using single-molecule real-time sequencing and a meta-assembly approach, we obtained one of the most comprehensive plant genomes to date. Diversity analyses highlighted the mosaic origin of 'La France', one of the first hybrids combining the growth vigor of European species and the recurrent blooming of Chinese species. Genomic segments of Chinese ancestry identified new candidate genes for recurrent blooming. Reconstructing regulatory and secondary metabolism pathways allowed us to propose a model of interconnected regulation of scent and flower color. This genome provides a foundation for understanding the mechanisms governing rose traits and should accelerate improvement in roses, Rosaceae and ornamentals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
The genomic floral language of rose.Nat Genet. 2018 Jun;50(6):770-771. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0141-9. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 29844433 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A high-quality genome sequence of Rosa chinensis to elucidate ornamental traits.Nat Plants. 2018 Jul;4(7):473-484. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0166-1. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Nat Plants. 2018. PMID: 29892093 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptomics identifies patterns of selection in roses.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Dec 22;18(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1585-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30579326 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and gene expression analysis during flower blooming in Rosa chinensis 'Pallida'.Gene. 2014 Apr 25;540(1):96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.02.008. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24530310
-
Genetics and genomics of flower initiation and development in roses.J Exp Bot. 2013 Feb;64(4):847-57. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers387. Epub 2013 Jan 29. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 23364936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and Biochemical Aspects of Floral Scents in Roses.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 20;23(14):8014. doi: 10.3390/ijms23148014. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Trehalose-6-phosphate Synthase and Trehalose-6-phosphate Phosphatase Gene Families in Rose (Rosa hybrida cv 'Carola') under Different Light Conditions.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 31;13(1):114. doi: 10.3390/plants13010114. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202423 Free PMC article.
-
Diversification of petal monoterpene profiles during floral development and senescence in wild roses: relationships among geraniol content, petal colour, and floral lifespan.Oecologia. 2021 Dec;197(4):957-969. doi: 10.1007/s00442-020-04710-z. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Oecologia. 2021. PMID: 32712874 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinism of prickles in rose.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 Nov;133(11):3017-3035. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03652-7. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 32734323
-
Flowering plants return to the sea….J Exp Bot. 2019 Sep 24;70(18):4591-4593. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz377. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 31552429 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Photinia serratifolia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 14;13(1):770. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24327-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36641495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Vries DP, Dubois L. Rose breeding : past, present, prospects. Acta Horticulturae. 1996;424:241–248.
-
- Martin M, Piola F, Chessel D, Jay M, Heizmann P. The domestication process of the Modern Rose: genetic structure and allelic composition of the rose complex. Theoretical-and-Applied-Genetics. 2001;102:398–404.
-
- Hurst CC. Notes on the orig in and evolution of our garden roses. Journal of the Royal Horticultural Society. 1941;66:73–82.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

