Engineering the entropy-driven free-energy landscape of a dynamic nanoporous protein assembly
- PMID: 29713036
- PMCID: PMC6056010
- DOI: 10.1038/s41557-018-0053-4
Engineering the entropy-driven free-energy landscape of a dynamic nanoporous protein assembly
Abstract
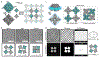
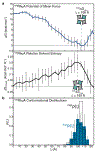
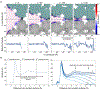
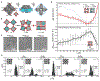
De novo design and construction of stimuli-responsive protein assemblies that predictably switch between discrete conformational states remains an essential but highly challenging goal in biomolecular design. We previously reported synthetic, two-dimensional protein lattices self-assembled via disulfide bonding interactions, which endows them with a unique capacity to undergo coherent conformational changes without losing crystalline order. Here, we carried out all-atom molecular dynamics simulations to map the free-energy landscape of these lattices, validated this landscape through extensive structural characterization by electron microscopy and established that it is predominantly governed by solvent reorganization entropy. Subsequent redesign of the protein surface with conditionally repulsive electrostatic interactions enabled us to predictably perturb the free-energy landscape and obtain a new protein lattice whose conformational dynamics can be chemically and mechanically toggled between three different states with varying porosities and molecular densities.
Figures
References
-
- Marsh JA & Teichmann SA Structure, Dynamics, Assembly, and Evolution of Protein Complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem 84, 551–575 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Song WJ & Tezcan FA A designed supramolecular protein assembly with in vivo enzymatic activity. Science 346, 1525–1528 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Yeates TO Geometric Principles for Designing Highly Symmetric Self-Assembling Protein Nanomaterials. Annu. Rev. Biophys 46, 23–42 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

