Accuracy and practicality of a portable ozone monitor for personal exposure estimates
- PMID: 29713236
- PMCID: PMC5918273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.11.036
Accuracy and practicality of a portable ozone monitor for personal exposure estimates
Abstract
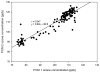
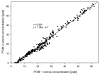
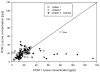
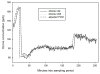
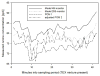
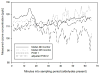
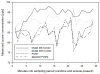
Accurate measurements of personal exposure to atmospheric pollutants such as ozone are important for understanding health risks. We tested a new personal ozone monitor (POM; 2B Technologies) for accuracy, precision, and ease of use. The POM's measurements were compared to simultaneous ozone measurements from a 2B Model 205 monitor and a ThermoScientific 49i monitor, and multiple POMs were placed side-by-side to check precision. Tests were undertaken in a controlled environmental facility, outdoors, and in a private residence. Additionally, ten volunteers wore a POM for five days and answered a questionnaire about its ease of use. The POM measured ozone accurately compared to the 49i ozone monitor, with average relative differences of less than 8%. In the controlled environment tests, the POM's ozone measurements did not change in the presence of additional atmospheric constituents with similar absorption lines to ozone, though there may have been a small decrease in precision and accuracy. Precision between POMs varied by environment (r2 = 0.98 outdoors; r2 = 0.3 to 0.9 in controlled lab conditions). Volunteers reported that the POM was reasonably comfortable to wear, although all reported that they felt that it was too noisy. Overall, the POM is a viable option for personal ozone monitoring.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Are Keggin's POMs Charged Nanocolloids or Multicharged Anions?Langmuir. 2018 Feb 6;34(5):2026-2038. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b03640. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Langmuir. 2018. PMID: 29278508
-
Active and passive ozone samplers based on a reaction with a binary reagent.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 1994 Feb;(63):1-18; discussion 67-82. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 1994. PMID: 8185874
-
Using low-cost sensors to monitor indoor, outdoor, and personal ozone concentrations in Beijing, China.Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2020 Jan 1;22(1):131-143. doi: 10.1039/c9em00377k. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2020. PMID: 31714569
-
Changes in biologically active ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth's surface.J Photochem Photobiol B. 1998 Oct;46(1-3):5-19. doi: 10.1016/s1011-1344(98)00182-1. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1998. PMID: 9894350 Review.
-
Characteristics and applications of small, portable gaseous air pollution monitors.Environ Pollut. 2017 Apr;223:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.045. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Environ Pollut. 2017. PMID: 28162801 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-Time Ozone Sensor Based on Selective Oxidation of Methylene Blue in Mesoporous Silica Films.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 10;19(16):3508. doi: 10.3390/s19163508. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31405181 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone exposure and cardiovascular disease: A narrative review of epidemiology evidence and underlying mechanisms.Fundam Res. 2024 Mar 23;5(1):249-263. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2024.02.016. eCollection 2025 Jan. Fundam Res. 2024. PMID: 40166088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell ML. The use of ambient air quality modeling to estimate individual and population exposure for human health research: A case study of ozone in the Northern Georgia Region of the United States. Environ Int. 2006;32:586–593. - PubMed
-
- Brauer M, Brook JR. Ozone personal exposures and health effects for selected groups residing in the Fraser Valley. Atmospheric Environment. 1997;31:2113–2121.
-
- Cao T, Thompson JE. Personal monitoring of ozone exposure: A fully portable device for under $150 USD cost. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2016;224:936–943.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
