IL-33/IL-31 Axis: A Potential Inflammatory Pathway
- PMID: 29713240
- PMCID: PMC5866851
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/3858032
IL-33/IL-31 Axis: A Potential Inflammatory Pathway
Abstract
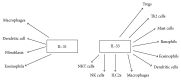
Cytokines play an important role in the regulation of the immune system (adaptive and innate). Given their importance in proinflammatory processes, cytokines have been used for understanding the pathogenesis and as biomarkers in many diseases. IL-31 and IL-33 are still considered novel cytokines. IL-31 controls signalling and regulates a huge amount of biological functions: it induces proinflammatory cytokines, regulates cell proliferation, and is involved also in tissue remodelling. On the other hand, IL-33 has been identified as an "alarmin" released from the epithelial cells and from different human tissues and organs after a damage following, that is, an inflammatory process. The aim of this literature review is to strengthen the hypothesis about an IL-31/IL-33 axis by evaluating the most recent studies linking these two cytokines. Literature data showed that, in many cases, IL-31 and IL-33 are linked to each other and that their expression is correlated with disease severity. The presence of one interleukin might stimulate the induction of the other, amplifying inflammation and the consequent detrimental processes. In a near future, influencing their balance could be helpful in modulating the first responses of the immune system in order to prevent the development of many inflammation-related diseases.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

