An Integrated Proteomics and Bioinformatics Approach Reveals the Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Carnosic Acid
- PMID: 29713284
- PMCID: PMC5911474
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00370
An Integrated Proteomics and Bioinformatics Approach Reveals the Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Carnosic Acid
Abstract
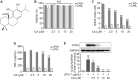
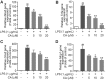
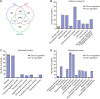
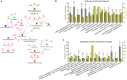
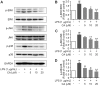
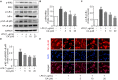
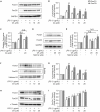
Drastic macrophages activation triggered by exogenous infection or endogenous stresses is thought to be implicated in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases. Carnosic acid (CA), a natural phenolic diterpene extracted from Salvia officinalis plant, has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory activity. However, its role in macrophages activation as well as potential molecular mechanism is largely unexplored. In the current study, we sought to elucidate the anti-inflammatory property of CA using an integrated approach based on unbiased proteomics and bioinformatics analysis. CA significantly inhibited the robust increase of nitric oxide and TNF-α, downregulated COX2 protein expression, and lowered the transcriptional level of inflammatory genes including Nos2, Tnfα, Cox2, and Mcp1 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, a murine model of peritoneal macrophage cell line. The LC-MS/MS-based shotgun proteomics analysis showed CA negatively regulated 217 LPS-elicited proteins which were involved in multiple inflammatory processes including MAPK, nuclear factor (NF)-κB, and FoxO signaling pathways. A further molecular biology analysis revealed that CA effectually inactivated IKKβ/IκB-α/NF-κB, ERK/JNK/p38 MAPKs, and FoxO1/3 signaling pathways. Collectively, our findings demonstrated the role of CA in regulating inflammation response and provide some insights into the proteomics-guided pharmacological mechanism study of natural products.
Keywords: FoxO1/3 pathway; IKKβ/IκB-α/NF-κB pathway; MAPK pathway; anti-inflammatory; carnosic acid; proteomics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 15;387:114846. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114846. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31790703
-
Gallic Acid-g-Chitosan Modulates Inflammatory Responses in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells Via NF-κB, AP-1, and MAPK Pathways.Inflammation. 2016 Feb;39(1):366-374. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0258-2. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26412258
-
The p38 MAPK inhibitor JLU1124 inhibits the inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide through the MAPK-NF-κB pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Nov;17(3):785-92. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24070708
-
Tanshinone IIA inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells: possible involvement of the NIK-IKK, ERK1/2, p38 and JNK pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug 7;542(1-3):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.044. Epub 2006 May 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16797002
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of the six compounds isolated from Nauclea officinalis Pierrc ex Pitard, and molecular mechanism of strictosamide via suppressing the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 20;196:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.007. Epub 2016 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27989509
Cited by
-
Potential of Natural Products as Therapeutic Agents for Inflammatory Diseases.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2024;23(3):149-163. doi: 10.2174/0118715230307969240614102321. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38984571 Review.
-
Natural Compounds of Salvia L. Genus and Molecular Mechanism of Their Biological Activity.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 27;11(12):3151. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123151. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Study of the Protective Effect of Bushen Huoxue Prescription on Cerebral Microvascular Endothelia Based on Proteomics and Bioinformatics.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 6;2022:2545074. doi: 10.1155/2022/2545074. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35035499 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosic acid nanocluster-based framework combined with PD-1 inhibitors impeded tumorigenesis and enhanced immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Jan 6;24(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01286-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. Retraction in: Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Feb 28;25(1):48. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01558-5. PMID: 38182693 Retracted.
-
Multi-Target Effects of ß-Caryophyllene and Carnosic Acid at the Crossroads of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodegeneration: From Oxidative Stress to Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;11(6):1199. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061199. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

