Intestinal duplication revealed by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
- PMID: 29713360
- PMCID: PMC5924845
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2018.61.4.132
Intestinal duplication revealed by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
Abstract
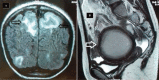
We report a unique case of intestinal duplication detected on posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in a 13-year-old girl. She was admitted to the pediatric Emergency Department because of generalized seizures. Radiological assessment revealed a large, well-defined, thick-walled cystic lesion in the mid abdomen, suggestive of duplication cyst associated to a PRES. Exploration confirmed the diagnosis of ileal duplication cyst, and the mass was resected. The postoperative course was uneventful. Both hypertension and neurological dysfunction resolved after the mass resection. A followup brain magnetic resonance imaging was performed 9 months later and showed complete resolution of the cerebellar changes. Although extrinsic compression of the retroperitoneal structures has not been reported in the literature as a complication of duplication cyst, we strongly believe that this is the most logical and plausible hypothesis that would explain the pathogenesis of PRES in our patient.
Keywords: Cyst; Hypertension; Ileum; Metoclopramide; Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Gümüş H, Per H, Kumandaş S, Yikilmaz A. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in childhood: report of nine cases and review of the literature. Neurol Sci. 2010;31:125–131. - PubMed
-
- Zuccoli G, Fitzgerald RT, Nardone R, Furtado AD, Abdel-Hamid H. The link between arterial blood pressure and vasogenic edema in pediatric PRES. Neuroradiology. 2015;57:865–866. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

