Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage
- PMID: 29713393
- PMCID: PMC5913875
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-018-0492-1
Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage
Abstract
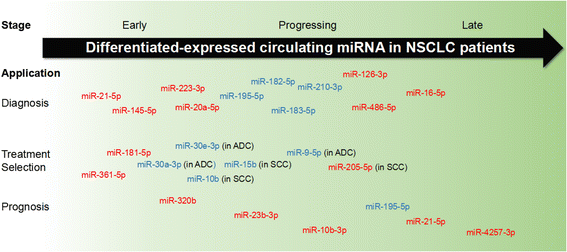
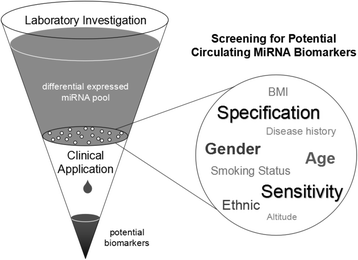
MicroRNAs are endogenous single-stranded non-coding small RNA molecules that can be secreted into the circulation and exist stably. They usually exhibit aberrant expression under different physiological and pathological conditions. Recently, differentially expressed circulating microRNAs were focused on as potential biomarkers for cancer screening. We herein review the role of circulating microRNAs for cancer diagnosis, tumor subtype classification, chemo- or radio-resistance monitoring, and outcome prognosis. Moreover, circulating microRNAs still have several issues hindering their reliability for the practical clinical application. Future studies need to elucidate further potential application of circulating microRNAs as specific and sensitive markers for clinical diagnosis or prognosis in cancers.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Circulating microRNA; Diagnosis; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis.Life Sci. 2020 May 1;248:117473. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117473. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32114007 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs: Biomarkers of disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2021 May;516:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.01.008. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Clin Chim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33485903 Review.
-
Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Lung Cancer.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020;215:299-318. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-26439-0_16. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31605236 Review.
-
Review of recent efforts to discover biomarkers for early detection, monitoring, prognosis, and prediction of treatment responses of patients with gastric cancer.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jul;12(7):657-670. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2018.1489233. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29902383 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs: potential biomarkers for common malignancies.Biomark Med. 2015;9(2):131-51. doi: 10.2217/bmm.14.102. Biomark Med. 2015. PMID: 25689901 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Genotyping Detection of Fragmented Nucleic Acids.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;14(10):465. doi: 10.3390/bios14100465. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Epigenetic miRNA Relationships in Human Cancer and Potential as Therapeutic Targets.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 11;12(10):2922. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102922. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Physically Active Status Affects the Circulating Profile of Cancer-Associated miRNAs.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 30;11(5):820. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050820. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946605 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterial infection-induced miR-206 inhibits protective neutrophil recruitment via the CXCL12/CXCR4 signalling axis.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Apr 7;17(4):e1009186. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009186. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33826679 Free PMC article.
-
An Insight into miR-1290: An Oncogenic miRNA with Diagnostic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 22;23(3):1234. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031234. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

