The Effects of Exposure to Mephedrone During Adolescence on Brain Neurotransmission and Neurotoxicity in Adult Rats
- PMID: 29713996
- PMCID: PMC6154178
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-018-9908-0
The Effects of Exposure to Mephedrone During Adolescence on Brain Neurotransmission and Neurotoxicity in Adult Rats
Erratum in
-
Correction to: the Effects of Exposure to Mephedrone During Adolescence on Brain Neurotransmission and Neurotoxicity in Adult Rats.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jul;36(1):218. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00023-z. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30905052 Free PMC article.
Abstract
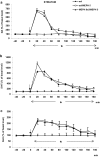
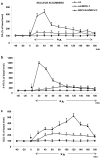
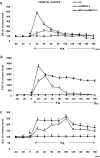
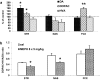
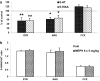
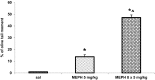
According to the European Drug Report (2016), the use of synthetic cathinones, such as mephedrone, among young people has rapidly increased in the last years. Studies in humans indicate that psychostimulant drug use in adolescence increases risk of drug abuse in adulthood. Mephedrone by its interaction with transporters for dopamine (DAT) and serotonin (SERT) stimulates their release to the synaptic cleft. In animal studies, high repeated doses of mephedrone given to adolescent but not adult mice or rats induced toxic changes in 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) neurons. The aim of our study was to investigate the effects of mephedrone given in adolescence on brain neurotransmission and possible neuronal injury in adult rats. Adolescent male rats were given mephedrone (5 mg/kg) for 8 days. In vivo microdialysis in adult rats showed an increase in dopamine (DA), 5-HT, and glutamate release in the nucleus accumbens and frontal cortex but not in the striatum in response to challenge dose in animals pretreated with mephedrone in adolescence. The 5-HT and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid contents decreased in the striatum and nucleus accumbens while DA turnover rates were decreased in the striatum and nucleus accumbens. The oxidative damage of DNA assessed with the alkaline comet assay was found in the cortex of adult rats. Therefore, the administration of repeated low doses of mephedrone during adolescence does not seem to induce injury to 5-HT and DA neurons. The oxidative stress seems to be responsible for possible damage of cortical cell bodies which causes maladaptive changes in serotonergic and dopaminergic neurons.
Keywords: Adolescence; Mephedrone; Microdialysis; Neurotoxicity; Neurotransmitters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Experimental study of methamphetamine psychosis--role of glutamate and nitric oxide in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotoxicity in the rat brain].Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 1997 Jan;72(1):113-26. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 1997. PMID: 9086367 Japanese.
-
Neurotoxicity Induced by Mephedrone: An up-to-date Review.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):738-749. doi: 10.2174/1570159X14666161130130718. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27908258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone prevents while methylone enhances methamphetamine-induced damage to dopamine nerve endings: β-ketoamphetamine modulation of neurotoxicity by the dopamine transporter.J Neurochem. 2015 Apr;133(2):211-22. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13048. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25626880 Free PMC article.
-
4-Methylmethcathinone (mephedrone): neuropharmacological effects of a designer stimulant of abuse.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Nov;339(2):530-6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.184119. Epub 2011 Aug 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21810934 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxicology of Synthetic Cathinone Analogs.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017;32:209-230. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_21. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27753008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Central Effects of the Designer Drug Mephedrone in Mice-Basic Studies.Brain Sci. 2022 Jan 30;12(2):189. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020189. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35203952 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropharmacology of Synthetic Cathinones.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;252:113-142. doi: 10.1007/164_2018_178. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30406443 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Co-Administration Changes Mephedrone-Induced Alterations of Neuronal Activity.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 28;12:679759. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.679759. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995109 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into Glutamatergic Involvement in Rewarding Effects of Mephedrone in Rats: In Vivo and Ex Vivo Study.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Sep;58(9):4413-4424. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02404-y. Epub 2021 May 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34021482 Free PMC article.
-
Psychoactive Drugs-From Chemical Structure to Oxidative Stress Related to Dopaminergic Neurotransmission. A Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 4;10(3):381. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030381. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anneken JH, Angoa-Pérez M, Kuhn DM. 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone prevents while methylone enhances methamphetamine-induced damage to dopamine nerve endings: β-ketoamphetamine modulation of neurotoxicity by the dopamine transporter. J Neurochem. 2015;133:211–222. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

