Intratumoral Spatial Heterogeneity at Perfusion MR Imaging Predicts Recurrence-free Survival in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
- PMID: 29714680
- PMCID: PMC6029132
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2018172462
Intratumoral Spatial Heterogeneity at Perfusion MR Imaging Predicts Recurrence-free Survival in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Abstract
Purpose To characterize intratumoral spatial heterogeneity at perfusion magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and investigate intratumoral heterogeneity as a predictor of recurrence-free survival (RFS) in breast cancer. Materials and Methods In this retrospective study, a discovery cohort (n = 60) and a multicenter validation cohort (n = 186) were analyzed. Each tumor was divided into multiple spatially segregated, phenotypically consistent subregions on the basis of perfusion MR imaging parameters. The authors first defined a multiregional spatial interaction (MSI) matrix and then, based on this matrix, calculated 22 image features. A network strategy was used to integrate all image features and classify patients into different risk groups. The prognostic value of imaging-based stratification was evaluated in relation to clinical-pathologic factors with multivariable Cox regression. Results Three intratumoral subregions with high, intermediate, and low MR perfusion were identified and showed high consistency between the two cohorts. Patients in both cohorts were stratified according to network analysis of multiregional image features regarding RFS (log-rank test, P = .002 for both). Aggressive tumors were associated with a larger volume of the poorly perfused subregion as well as interaction between poorly and moderately perfused subregions and surrounding parenchyma. At multivariable analysis, the proposed MSI-based marker was independently associated with RFS (hazard ratio: 3.42; 95% confidence interval: 1.55, 7.57; P = .002) adjusting for age, estrogen receptor (ER) status, progesterone receptor status, human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2) status, tumor volume, and pathologic complete response (pCR). Furthermore, imaging helped stratify patients for RFS within the ER-positive and HER2-positive subgroups (log-rank test, P = .007 and .004) and among patients without pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (log-rank test, P = .003). Conclusion Breast cancer consists of multiple spatially distinct subregions. Imaging heterogeneity is an independent prognostic factor beyond traditional risk predictors.
© RSNA, 2018 Online supplemental material is available for this article.
Figures




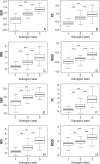
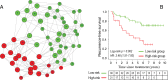
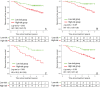

Comment in
-
Perfusion MR Imaging of Breast Cancer: Insights Using "Habitat Imaging".Radiology. 2018 Jul;288(1):36-37. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180271. Epub 2018 May 1. Radiology. 2018. PMID: 29714676 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gralow JR, Burstein HJ, Wood W, et al. . Preoperative therapy in invasive breast cancer: pathologic assessment and systemic therapy issues in operable disease. J Clin Oncol 2008;26(5):814–819. - PubMed
-
- Zardavas D, Irrthum A, Swanton C, Piccart M. Clinical management of breast cancer heterogeneity. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2015;12(7):381–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

